Figure 5.
Cortical Astroglia Nucleofected with NEUROG2 Integrate as Pyramidal Cell-like iNs In Vivo
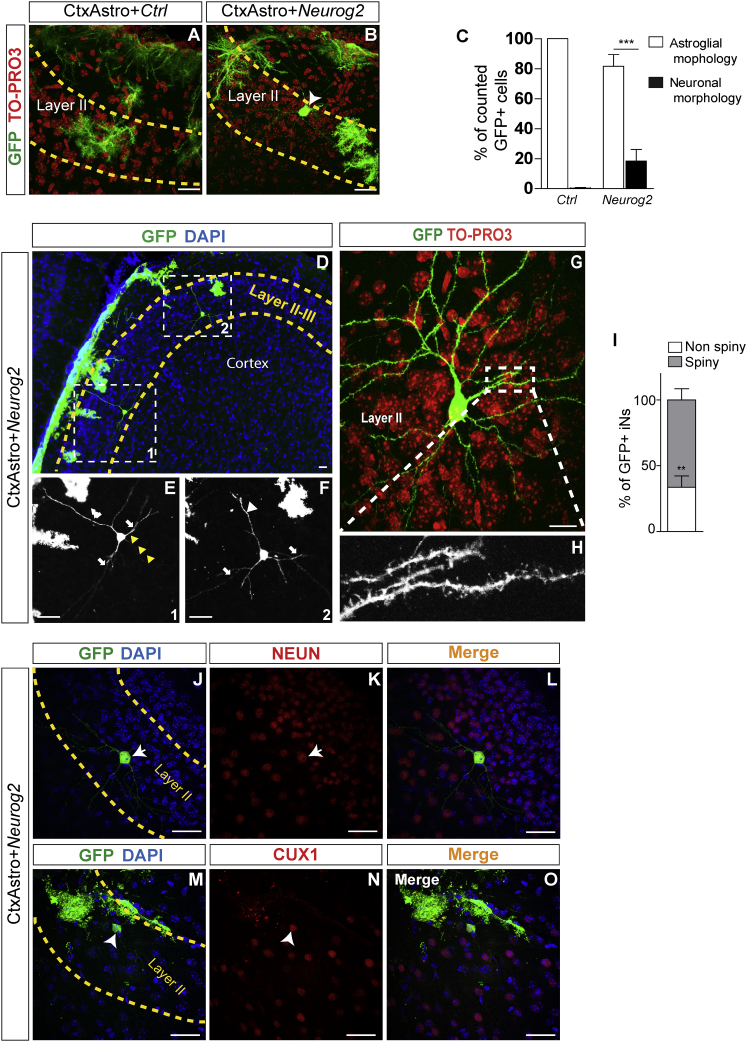
(A and B) Examples of GFP+ CtxAstro 20 days post transplantation (dpt) in the postnatal mouse cerebral cortex. Observe the astrocytic morphology of CtxAstro nucleofected with control plasmid (Ctrl) in the cortical layer II (A), and the presence of GFP+ cells with neuronal morphology in animals transplanted with CtxAstro nucleofected with NEUROG2 (B, arrowhead).
(C) Quantification of cells showing astroglial or neuronal morphology 20 days after transplantation. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(D–H) Examples of GFP+ pyramidal-like iNs observed in the cerebral cortex following transplantation of CtxAstro nucleofected with NEUROG2. Note the typical pyramidal cell morphology of iNs in layers II and III of the host cerebral cortex (D, dashed boxes). (E and F) Magnification of dashed boxes shown in (D) revealing the apical dendrite (white arrowheads), basal dendrites (white arrows), and axonal process of iNs (yellow arrowheads). (G) Example of iN in layer II of the cerebral cortex showing spiny dendrites (dashed box magnified in H), suggestive of a glutamatergic identity.
(I) Quantification of spiny and non-spiny iNs in the cerebral cortex of host animals. ∗∗p < 0.01.
(J–L) GFP+ iN 20 dpt expressing the mature neuronal marker NEUN (J and K, white arrows).
(M–O) GFP+ iN 20 dpt expressing the transcription factor CUX1 (M–N, white arrowheads). Nuclei are stained with either DAPI (blue) or TO-PRO3 (red).
Statistical test in (C) and (I): Student’s t test (mean ± SEM). n = 5 animals/condition. WM, white matter. Scale bars, 50 μm. See also Figure S7.