Figure 6.
Cerebellar and Cortical Astroglia-Derived iNs Integrate in the Postnatal Olfactory Bulb
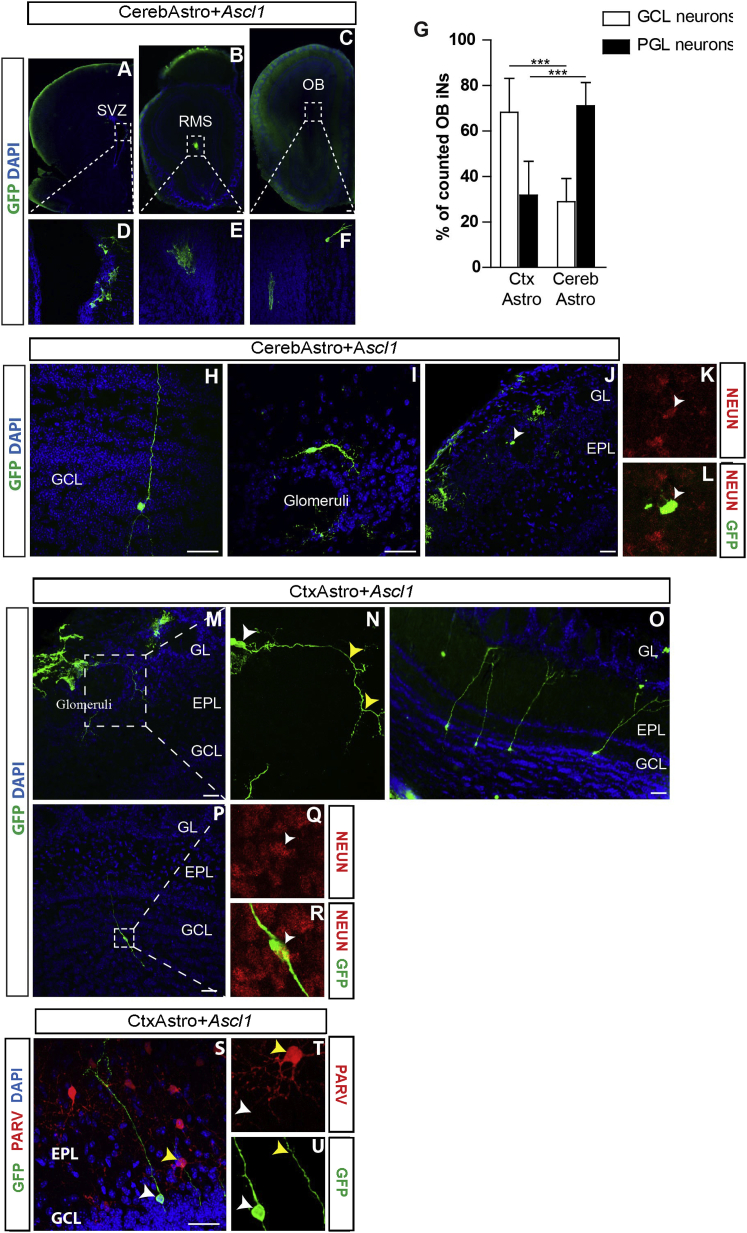
(A–F) Coronal sections obtained from a mouse brain 30 dpt of CerebAstro nucleofected with ASCL1. GFP+ cells grafted in the SVZ (A), anterior RMS (B), and OB (C). Dashed boxes in (A) to (C) are magnified in (D) to (F).
(G) Quantification of iNs in the GCL or PGL of the OB following transplantation of CerebAstro or CtxAstro nucleofected with ASCL1 in the SVZ. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(H–L) Examples of GFP+ OB iNs derived from CerebAstro nucleofected with ASCL1. Note the typical morphology of granular (H) or periglomerular (I) OB neuron adopted by iNs. Observe also the expression of NEUN (J–L, white arrowhead).
(M–R) Examples of GFP+ iNs in the OB, derived from CtxAstro nucleofected with ASCL1. Observe the typical morphologies of iNs in the PGL (N, white arrowhead points to the cell soma and yellow arrowheads indicate the processes of the same cell) and GCL (O and P). (Q and R) Example of a granular-like iN expressing NEUN (white arrowheads).
(S) Immunohistochemistry for PARV (red) and GFP (green) in the OB of a transplanted animal.
(T and U) Magnification of cells in (S): PARV+ cell (yellow arrowheads), GFP+/PARV− iNs (white arrowheads).
PARV, PARVALBUMIN; SVZ, subventricular zone; RMS, rostral migratory stream; OB, olfactory bulb; GL, glomerular layer; EPL, external plexiform layer; GCL, granule cell layer. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Statistical test: two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test (mean ± SEM). N = 5 animals/condition.
Scale bars, 50 μm. See also Figure S7.