Figure 6.
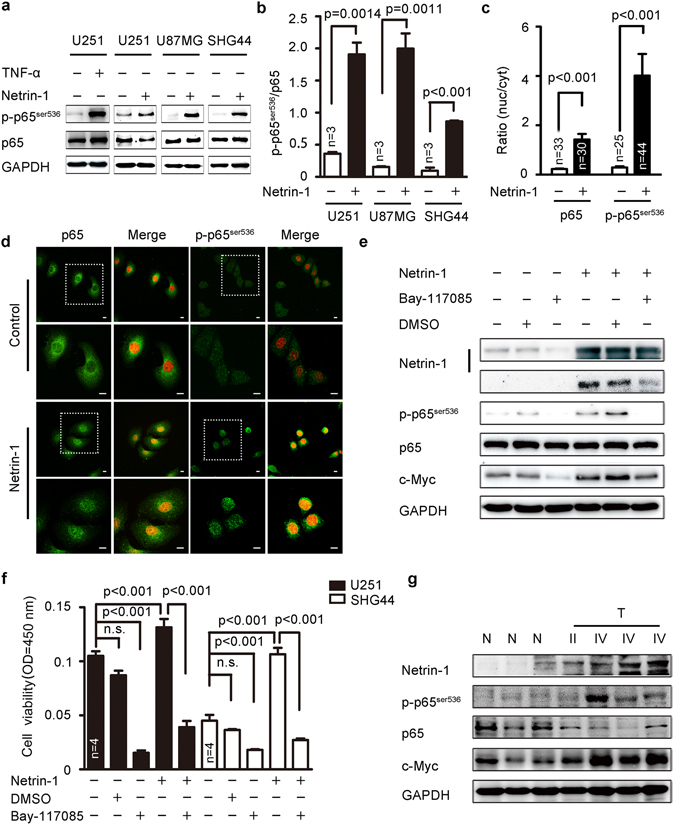
Netrin-1 could activate of the NF-κB signaling pathway. (a) Western blotting analyses of p65ser536 phosphorylation in U87MG, U251 and SHG44 cells in response to netrin-1 stimulation. TNFα was used as a positive control. (b) Quantification of p65ser536 phosphorylation using Gel-Pro Analyzer 4 software. Phosphorylation of p65ser536 was normalized to total of p65 expression. (c) Quantification of cytosolic and nuclear p65 and phosphorylation of p65ser536 immunofluorescence results using Image J. (d) Subcellular localization of p65 and p65ser536 phosphorylation in U251 cells in the absence or presence of netrin-1. DAPI staining is red. Scale bar: 10 μm. Boxed areas in the upper panels were magnified and shown in the corresponding lower panels. (e) U251 cells were pretreated with the NF-κB-specific inhibitor Bay117085 (15 µm/L) for 3 h prior to treatment with recombinant human netrin-1 for 30 min. Cells were pretreated with DMSO as a negative control. Netrin-1, p65ser536 and c-Myc were detected by western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (f) U251 and SHG44 cells were treated with the NF-κB-specific inhibitor Bay117085 (15 µm/L) for 3 h prior to treatment with recombinant human netrin-1 for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay. (g) Western blotting analyses of netrin-1, p65ser536, total p65 and c-Myc in glioma tumor tissues (T) and normal brain tissues (N) from clinical samples. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM. n.s., P > 0.05.
