Figure 7.
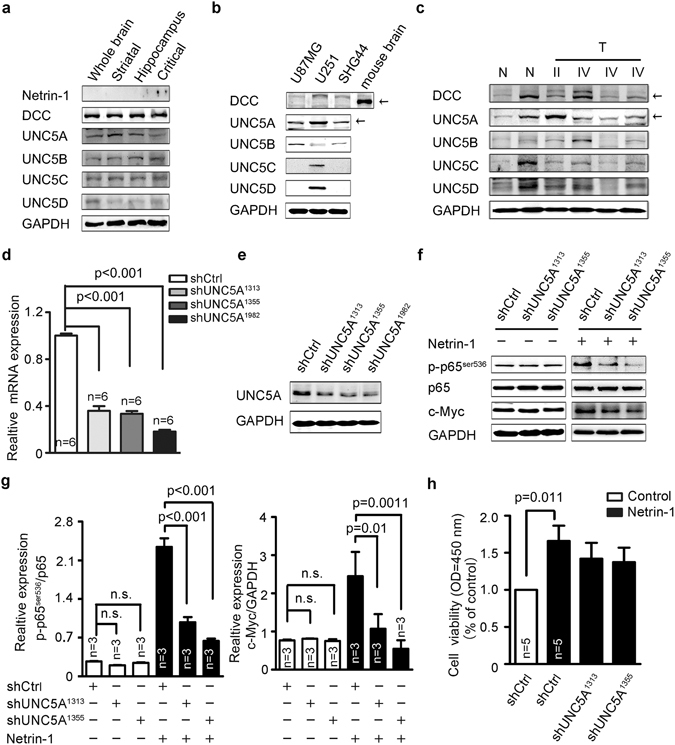
Netrin-1 activation of the NF-κB pathway was dependent on its canonical receptor UNC5A. (a) Western blotting analysis of canonical receptors of netrin-1 in the adult mouse brain. (b) Western blotting analysis of canonical receptors of netrin-1 in U87MG, U251 and SHG44 cells. (c) Western blotting analyses of canonical receptors of netrin-1 in glioma tumor tissues (T) and normal brain tissues (N) from clinical samples. (d and e) UNC5A mRNA and protein expression levels were determined by real-time PCR and western blotting in U251 cells infected with lentivirus expressing shCtrl or shUNC5A. (f) Western blotting analysis of p65ser536 and c-Myc in U251 cells infected with lentivirus expressing shCtrl or shUNC5A with or without netrin-1 stimulation. (g) Quantification of p65ser536 phosphorylation using Gel-Pro Analyzer 4 software. Phosphorylation of NF-κB p65ser536 was normalized to total p65, and c-Myc was normalized to GAPDH. (h) CCK-8 assays revealed that the addition of netrin-1 promoted cell proliferation. On the contrary, silencing of UNC5A blocked netrin-1-induced cell proliferation. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM.
