Figure 6.
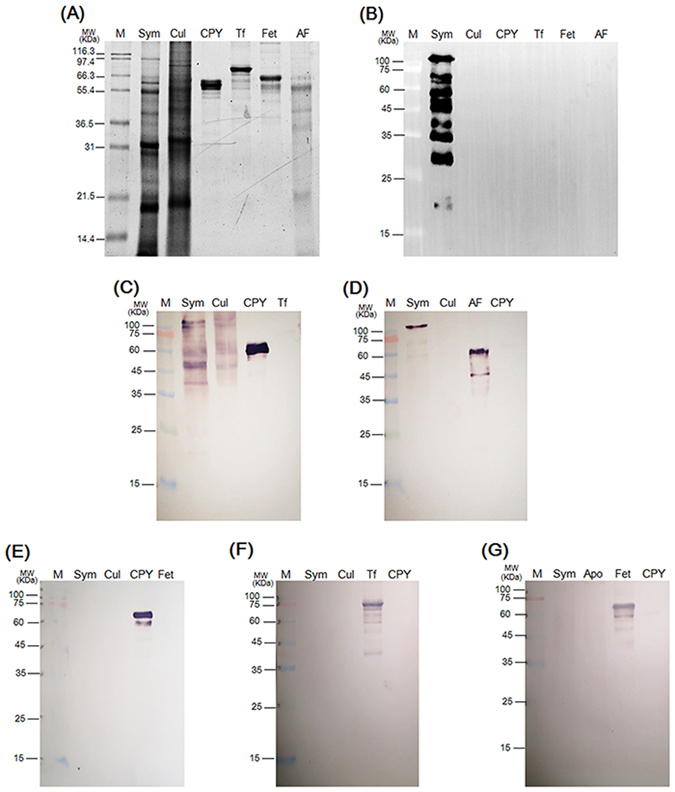
Detection of terminal sugar residues of glycoproteins in symbiotic and free-living Symbiodinium. (A) Six proteins (two Symbiodinium proteins and four control glycoproteins) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and stained with SYPRO® Ruby. (B) Western blotting was performed using the 2–6F mAb. Five types of lectin-conjugated alkaline phosphatase, (C) GNA, (D) PNA, (E) MAA, (F) SNA, and (G) DSA, were used to detect different glycans. M: marker; Sym: total proteins of symbiotic Symbiodinium (clade C) freshly isolated from E. glabrescens; Cul: total proteins of cultured Symbiodinium CCMP 2466 (clade C); CPY: carboxypeptidase Y; Tf: transferrin; Fet: fetuin; AF: asialofetuin. Four control glycoproteins were used: CPY, Tf, Fet, and AF. For GNA, CPY is a positive control, and Tf is a negative control. For PNA, AF is a positive control, and CPY is a negative control. For MAA, CPY is a positive control, and Fet is a negative control. For SNA, Tf is a positive control, and CPY is a negative control. For DSA, Fet is a positive control, and CPY is a negative control.
