Abstract
Group A streptococci which produce streptolysin S contain a cellular precursor to streptolysin S in the membranes and cytoplasm which is activatable by blending in a Vortex mixer with glass beads and ribonucleic acid (RNA)-core (RNA preparation from yeast). Although no activation of precursor occurred when it was mixed with detergents, it was activated when blended with glass beads and detergents such as Tergitol NP-40 and Brij 35. Maximum activation of precursor was achieved in 1 to 2% detergent, in pH 6.5 buffer, and after 8 min of blending. Detergents Tween 20, 40, 60, and 80, Brij 56, and Lubrol WX also activated precursor, but, of all the hemolysin preparations, those with Tween 40 or 60 or Lubrol WX were the most stable. The addition of RNA-core during or after blending of precursor with detergents enhanced the titer and stability of the hemolysin. This was due in part to the association of the hemolytic moiety with RNA-core. Activation of precursor in the membrane was better with a detergent, whereas that in the cytoplasm was better with RNA-core. Therefore, precursor from two different cellular locations can be differentiated by the effects of RNA-core and detergents on precursor titer.
Full text
PDF
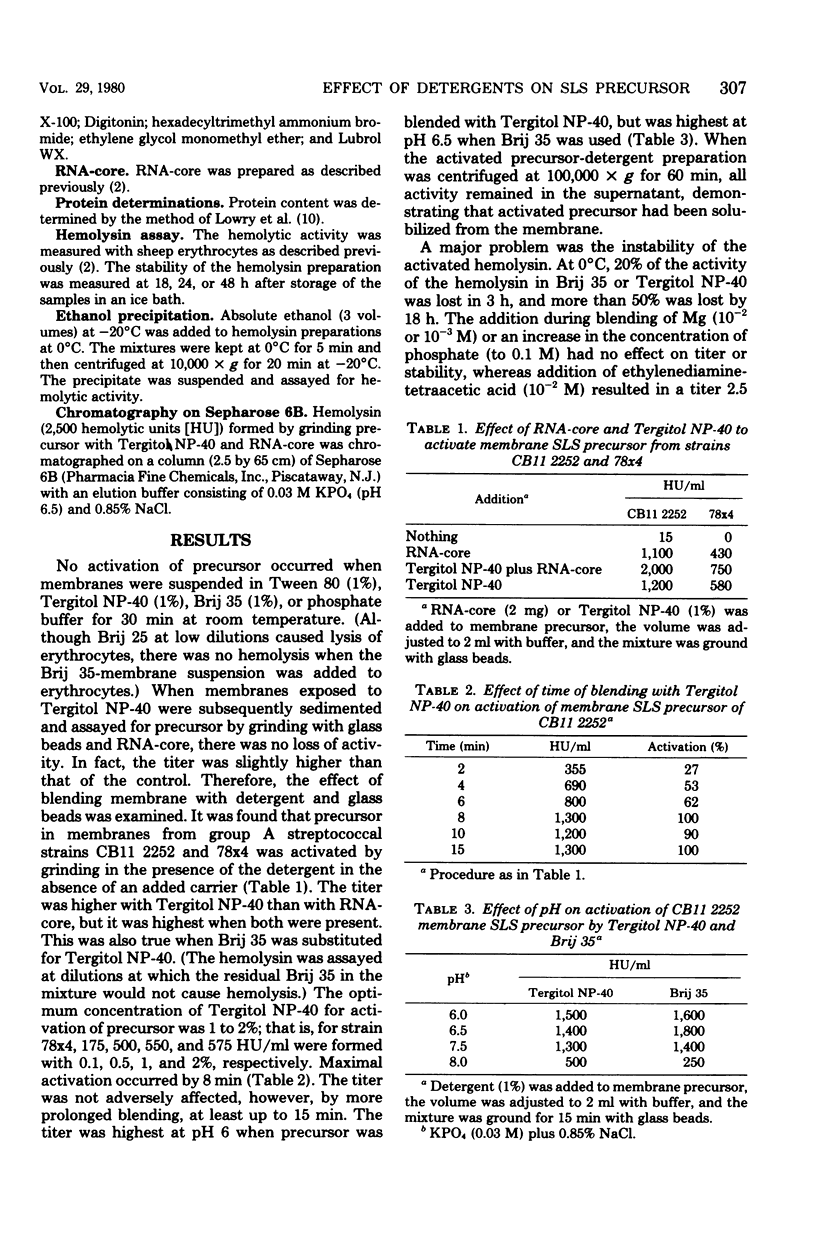
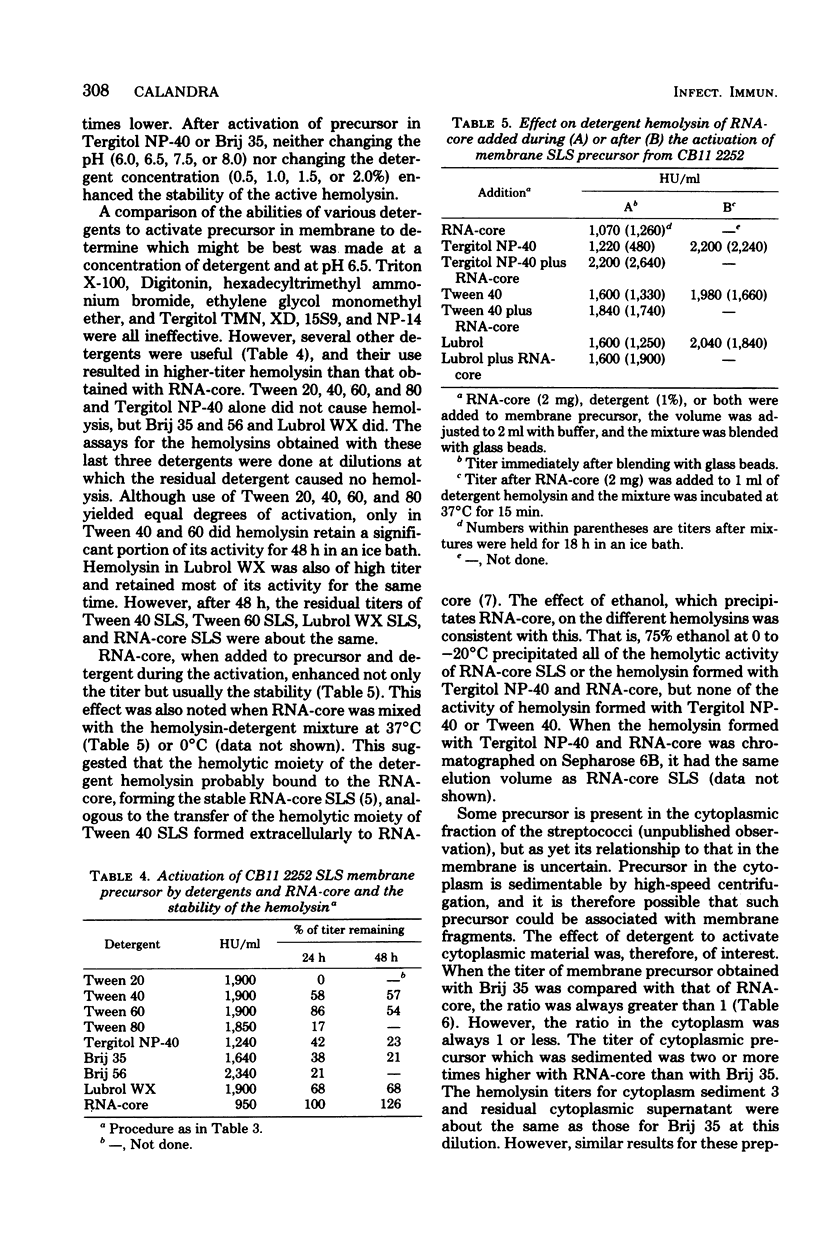


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calandra G. B., Oginsky E. L. Cellular streptolysin S-related hemolysins of group A Streptococcus C203S. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):13–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.13-28.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra G. B., Theodore T. S. Cellular location of streptolysin O. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):750–753. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.750-753.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra G. B., Whitt R. S., Cole R. M. Relationship of cellular potential hemolysin in group A streptococci to extracellular streptolysin S. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):813–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.813-817.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG I., GROSSOWICZ N. A cell-bound hemolysin of group A streptococci. Bull Res Counc Isr Sect E Exp Med. 1958 Dec;7E:237–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG I., HARRIS T. N. OXYGEN-STABLE HEMOLYSINS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI. II. CHROMATOGRAPHIC AND ELECTROPHORETIC STUDIES. J Exp Med. 1963 Dec 1;118:919–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.6.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Roy C., Jard S. A systematic study of effects of non-ionic detergens on solubilization and activity of pig kidney adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOYAMA J. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON STREPTOLYSIN S'. II. PROPERTIES OF A POLYPEPTIDE COMPONENT AND ITS ROLE IN THE TOXIN ACTIVITY. J Biochem. 1963 Aug;54:146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machtiger N. A., Fox C. F. Biochemistry of bacterial membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:575–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Reconstruction of biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;265(2):241–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokogawa K., Kawata S., Nishimura S., Ikeda Y., Yoshimura Y. Mutanolysin, bacteriolytic agent for cariogenic Streptococci: partial purification and properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):156–165. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


