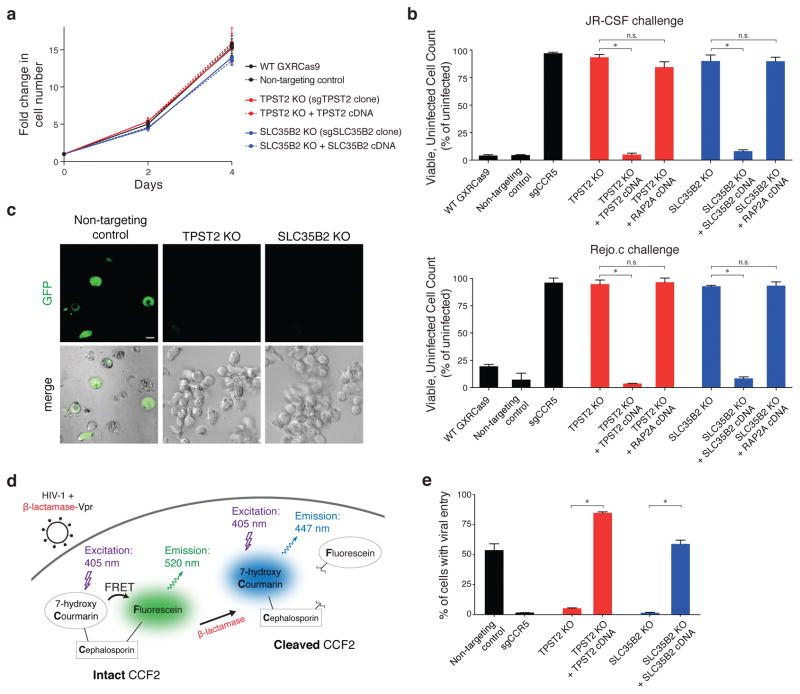
Figure 2. Loss of TPST2 or SLC35B2 confers strong protection against HIV infection and entry without compromising host cell viability.
(a) Normal proliferation of TPST2-null and SLC35B2-null GXRCas9 cells compared to wild-type cells, non-targeting sgRNA transduced cells, and cells with rescued TPST2 and SLC35B2 expression. Error bars represent standard deviation of six replicate wells.
(b) Virus challenge assay with JR-CSF (upper panel) and Rejo.C, a patient-derived transmitted/founder strain of HIV (lower panel). Three days following HIV infection (MOI = 1), viable, GFP-negative cells were counted and normalized to a mock-infected condition. Error bars represent standard deviation of triplicate wells. Error bars, s.d.; triplicate wells; * denotes P<0.01, Welch’s t-test. P-values as follows: JR-CSF – TPST2: *, P<0.0001 and ns, P=0.0637; SLC35B2: *, P=0.0009 and ns, P=0.9714; Rejo.c – TPST2: *, P=0.0005 and ns, P=0.6478; SLC35B2: *, P<0.0001 and ns, P=0.7751.
(c) Confocal microscopy of non-targeting control, TPST2-null, and SLC35B2-null GXRCas9 cells following HIV challenge. GFP is a reporter for productive HIV infection. Scale bar = 5 μm.
(d) HIV entry assay schematic. β-lactamase-Vpr fusion protein is packaged in HIV virions. Target cells are loaded with CCF2, a FRET donor/acceptor pair linked by a β-lactam ring. Upon viral fusion, the virus-delivered β-lactamase cleaves off the intracellular FRET acceptor, leading to an emission shift.
(e) HIV entry assay for TPST2-null and SLC35B2-null GXRCas9 cells compared to wild-type cells, non-targeting control cells, and cells with rescued TPST2 and SLC35B2 expression. Error bars, s.d.; triplicate wells; * denotes P<0.01, Welch’s t-test. P-values as follows: TPST2: *, P<0.0001; SLC35B2: *, P=0.0001.