Figure 2. Repertoire of somatic non-synonymous mutations of metaplastic breast cancers (MBCs) of different histologic subtypes.
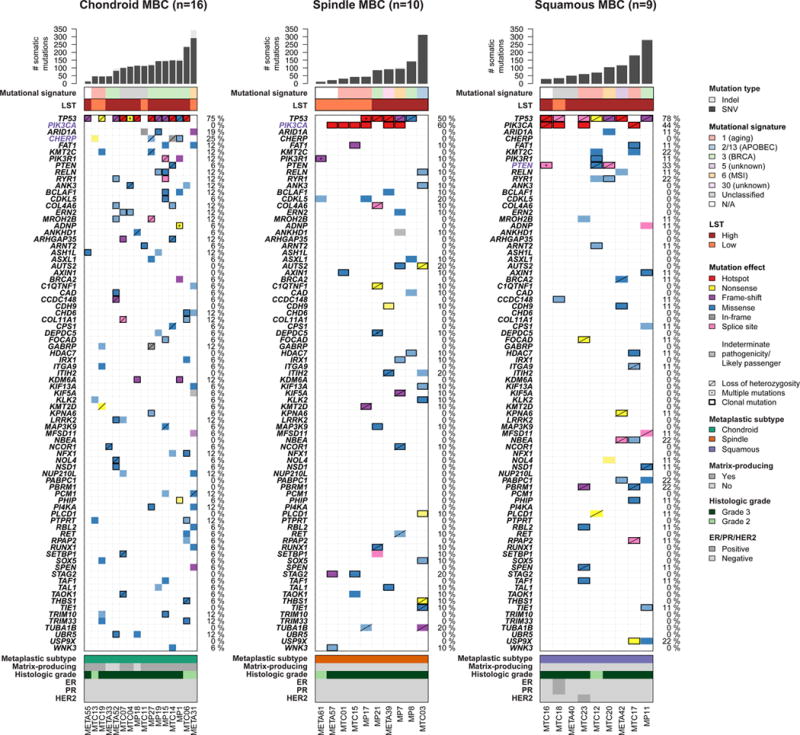
Non-synonymous somatic mutations identified in 16, ten and nine chondroid, spindle and squamous MBCs, respectively, by whole-exome sequencing are color-coded by their effect according to the legend, with hotspots (32) colored in red. Likely passenger mutations and mutations of indeterminate pathogenicity are marked using a hatched pattern. The presence of multiple non-synonymous mutations in the same gene is represented by an asterisk. The presence of loss of heterozygosity of the wild-type allele of a mutated gene is represented by a diagonal bar, and mutations found to be clonal by ABSOLUTE (24) are indicated by a black box. Genes recurrently mutated in MBCs and displaying at least one likely pathogenic mutation are presented. Genes highlighted in purple were significantly differentially altered in the given subtype of MBC. Percentages to the right of the mutation heatmaps indicate the percentage of cases affected by non-synonymous somatic mutations in a given gene. Bar charts (top) indicate the number of non-synonymous and synonymous somatic single nucleotide variants (SNVs), and the number of somatic insertions and deletions (indels) for each sample. The dominant mutational signatures (35, 36) were assigned using deconstructSigs (37). Large-scale transitions (LST)-high and -low status was determined in accordance with Popova et al (39).
