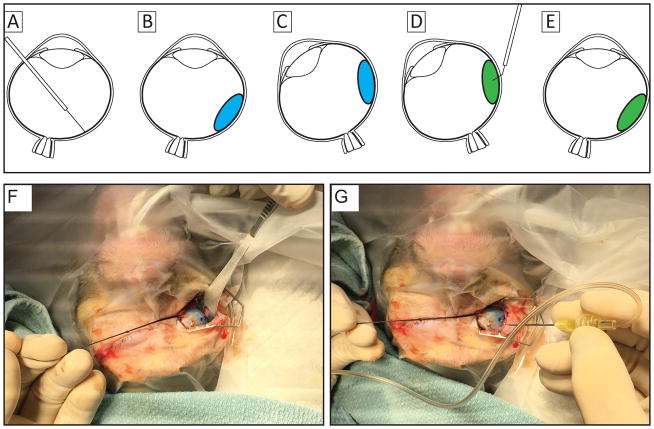
Figure 1.
Illustrations of the surgical approach for transscleral delivery of cell suspension resulting in high success rates that places cells within the subretinal space without leakage into the vitreous. (A) a subretinal bleb (panel B;blue; ~300 μL) is created using a 41g cannula. The location of the bleb is marked externally and the eye is rotated to ease access to location for injection (C), cells are injected into the subretinal bleb using a 30 gauge cannula (D; green). The eye is then returned to resting position (E) and examined using an indirect ophthalmoscope to ensure proper location of the delivered cells. Panel F illustrates rotation of the right eye and marking the location at which the injection cannula will be inserted, seen in panel G.