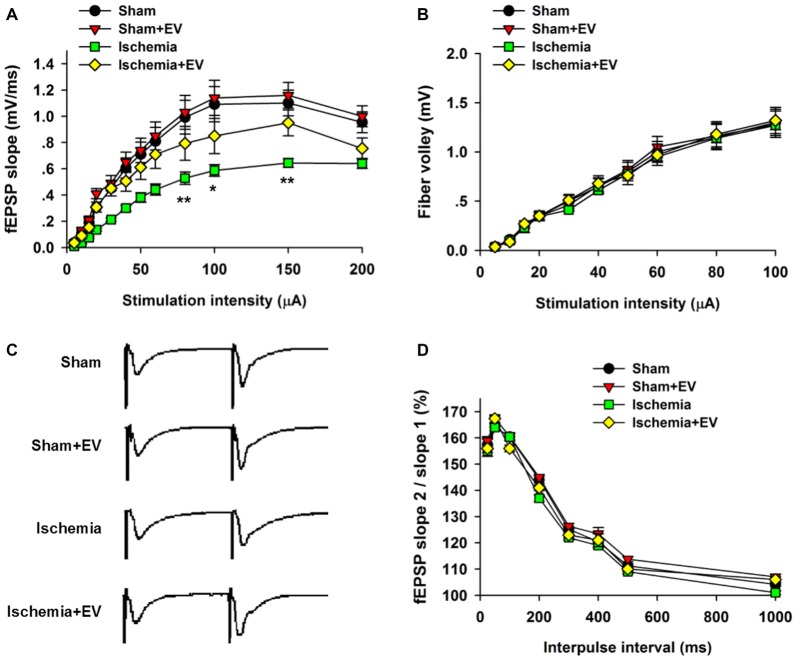
Figure 3.
Effects of ischemia and BMSC-EVs on basal properties of excitatory synaptic transmission in animals subjected to global ischemia. (A) Input-output (I/O) ratios of field excitatory post-synaptic potentials (fEPSPs) slope at Schaffer collateral to CA1 synapses were recorded from stratum radiatum in acute hippocampal slices (80 μA: sham = 0.99 ± 0.13, sham + EV = 1.03 ± 0.13, ischemia = 0.53 ± 0.05, ischemia + EV = 0.80 ± 0.12; 100 μA: sham = 1.10 ± 0.14, sham + EV = 1.15 ± 0.15, ischemia = 0.59 ± 0.04, ischemia + EV = 0.85 ± 0.14; 150 μA: sham = 1.10 ± 0.12, sham + EV = 1.16 ± 0.11, ischemia = 0.65 ± 0.04, ischemia + EV = 0.95 ± 0.11). (B) Fiber volley amplitude were recorded as a function of stimulus intensity. (C,D) BMSC-EVs does not alter release probability in mice subjected to global ischemia. fEPSPs evoked by paired pulse stimulation of Schaffer collaterals at 25, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 and 1000 ms were recorded. (C) shows representative fEPSP traces with 100 ms of inter-pulse interval. n = 15 neurons from four mice per group. Data show means ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA analysis followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.