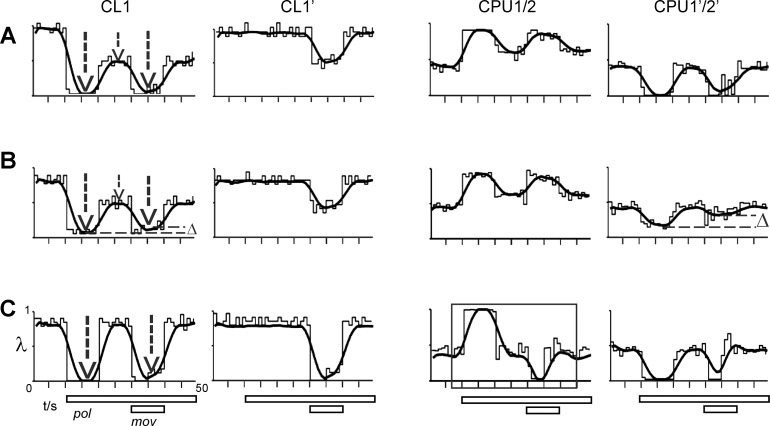
Fig. 6.
Variations in the responses of CL1 result in 3 different types of downstream-response to combined stimulation by compass and moving object stimuli. Conventions as in Fig. 5; plots of firing rate (λ) vs. time show the response of the CL1 cell in the driving (CL1) and driven (CL1′) channel and the corresponding output responses of the CPU1/2 and CPU1′/2′ cell. CPU1/2 responses are strongly determined by the temporal dynamics of the CL1 responses to polarized light. A: a strong phasic-tonic compass response in CL1 (1st and 2nd vertical arrow) results in an equally strong response to combined stimulation (3rd arrow) as well as in a regain of compass responses in CPU1/2 and CPU1′/2′ (reproduced from Fig. 5). B: a decrease in the tonic CL1 response (compare lengths of vertical arrows) leads to dampening (Δ, horizontal line) of the CL1 response to combined stimulation and of the regain of compass response in the driven CPU1′/2′. This in turn should correspond to a shallower slope of the regression lines in Fig. 4A. C: when the CL1 response to polarized light is purely phasic, inhibitory responses to the moving object occur in both CPU1/2 (box) and CPU1′/2′.