Figure 5.
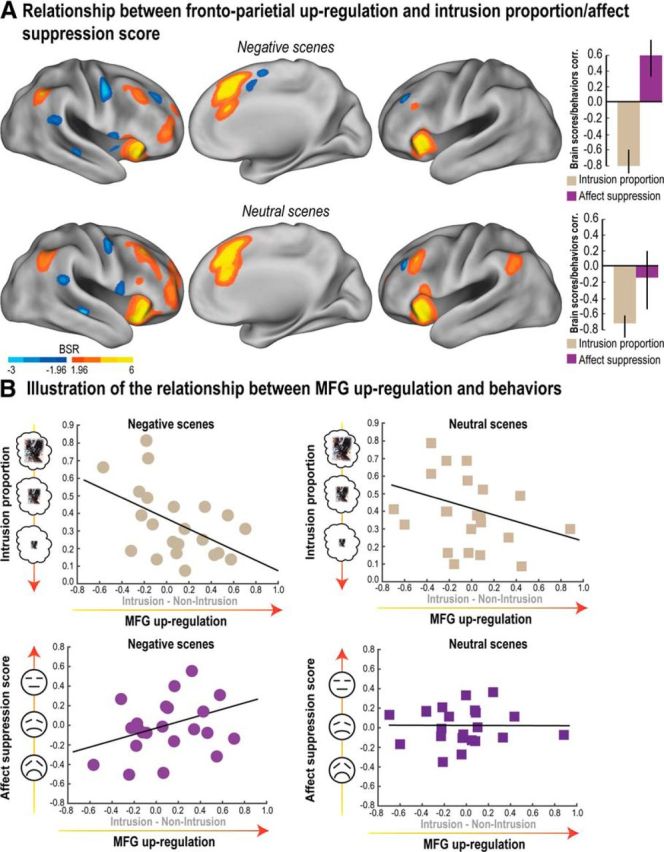
Relationship between neural markers of inhibitory control and the reduction of mnemonic awareness/affective response. Outcome of the PLS analysis for both Negative and Neutral scenes (conducted within the retrieval suppression network; see Materials and Methods) between intrusion-related upregulation (Intrusion − Non-Intrusion) and behavioral measures (intrusion proportion and affect suppression score). A, Voxels showing a significant pattern of brain/behavior correlations as revealed by the first (significant) LV were identified using a BSR threshold higher/lower than 1.96/−1.96, respectively (i.e., p < 0.05). Correlations between participants' brain scores and behavioral measures for the first significant LV are also reported in A. Error bars indicate bootstrapped 95% CI. Brain scores reflect the contribution of each participant to a given LV. The correlation between brain scores and behaviors thus reveals the meaning of the LV. B, Scatter plots observed in the right MFG illustrating the relationship captured by PLS analysis between the upregulation (Intrusion − Non-Intrusion) and behavioral scores for Negative and Neutral scenes. These findings reveal voxels whose upregulation is associated with reduced intrusion frequency for both Negative and Neutral scenes and also with increased affect suppression score only in the case of Negative scenes (reduced negative affect for suppressed images). BSR maps were rendered on the top of the PALS human surface using Caret software (Van Essen et al., 2001) (RRID:SCR_006260).
