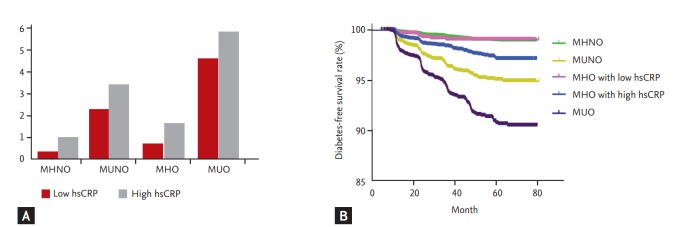
Figure 4.
Combined effect of the obese phenotypes and level of systemic inflammation on the incident rate of type 2 diabetes. (A) Data are the percentage (case/total number of each group). (B) Type 2 diabetes-free survival by Kaplan-Meier analysis according to baseline metabolic healthy, obesity state, and systemic inflammation (log-rank test, p < 0.001 for all three comparisons except metabolically healthy non-obesity [MHNO] with metabolically healthy obesity [MHO] with low systemic inflammation; p = 0.744). Modified from Jung et al. [21], with permission from Oxford University Press. MUNO, metabolically unhealthy non-obesity; MUO, metabolically unhealthy obesity; hsCRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.