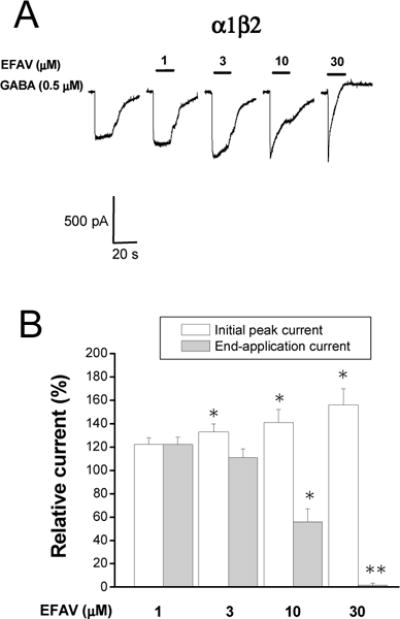
Figure 6. Effect of efavirenz on the GABA concentration-response curve recorded from α1β2γ2 (A&B) and α3β2γ2 (C&D) GABAA receptors stably expressed in HEK293 cells.
A&C, Representative traces showing whole-cell currents activated by different [GABA] in control and in the presence of efavirenz in α1β2γ2 (A) and α3β2γ2 (C). Note that Efavirenz modulated the response to a low [GABA] but did not affect the response to saturating [GABA] in both receptor configurations (A&C). B&D, Efavirenz significantly shifts the EC50 value for GABA without changing maximal currents. Currents are normalized to the maximal amplitude. EC50 values or Hill coefficients (in parentheses) were 36 ± 6.0 (1.5 ± 0.09) in control and 24 ± 5.8* μM (1.1 ± 0.09*) in presence of 10 μM efavirenz for α1β2γ2, and 34 ± 4.2 μM (0.96 ± 0.06) in control and in 89 ± 18* μM (0.84 ± 0.13) in the presence of 10 μM efavirenz for α3β2γ2. *, p<0.01, paired t-test, compared to the control, n=6–11.
