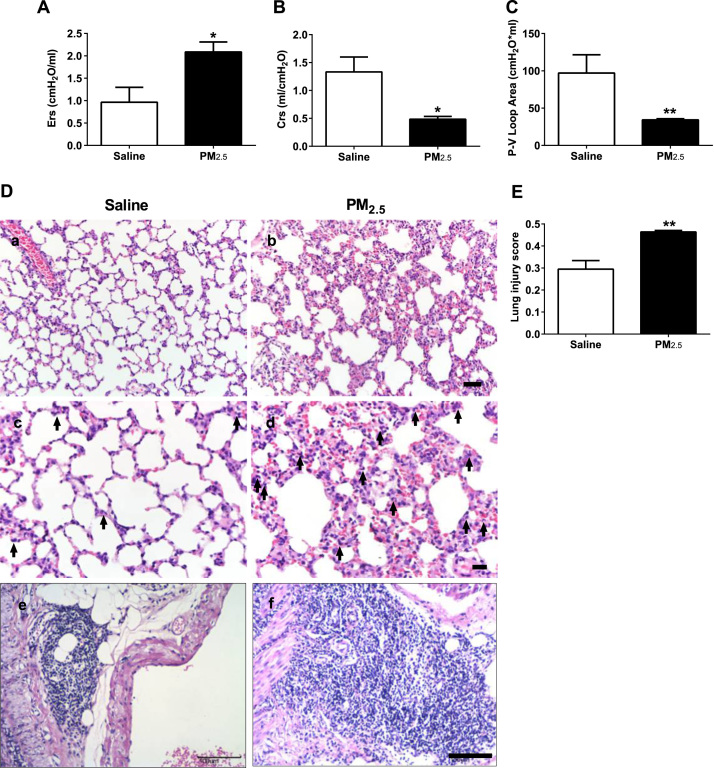
Fig. 2.
Intra-tracheal instillation of PM2.5induces acute pulmonary injury. (A) Elasticity of the respiratory system (Ers) of rats. (B) Compliance of the respiratory system (Crs) of rats. (C) Area of the P-V loop of rats. (D) Representative H.E. staining of pulmonary tissue of rats (Bars, a, b: 50 µm, c, d: 20 µm, e, f: 100 µm; Arrow, PMNs). (E) Lung injury score of rats. PM2.5 (45 mg/kg) was intra-tracheally instilled into rats on the 1st, 3rd and 6th days (n = 3–5). (A-C, E) All of the data are presented as the means ± SEM. Two-tailed Student's t-test: * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 compared with the saline instillation group.