Abstract
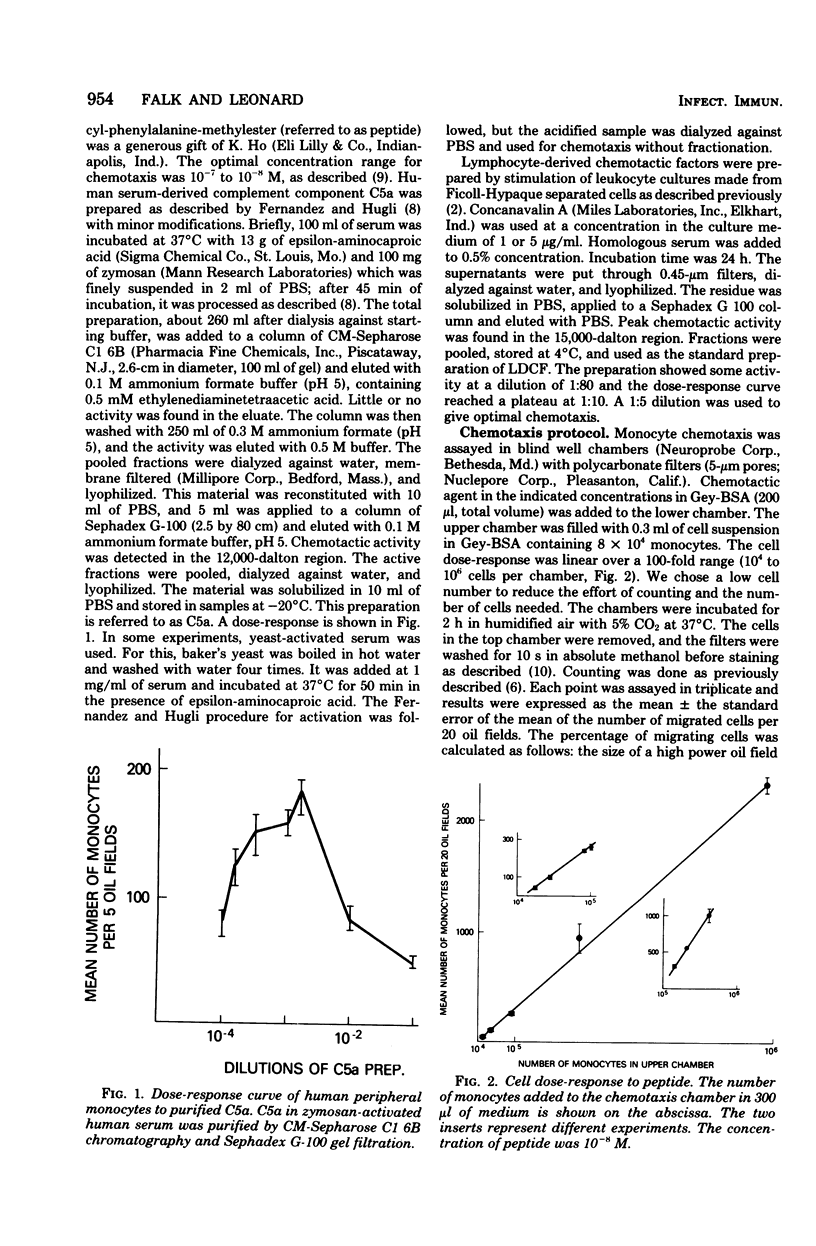
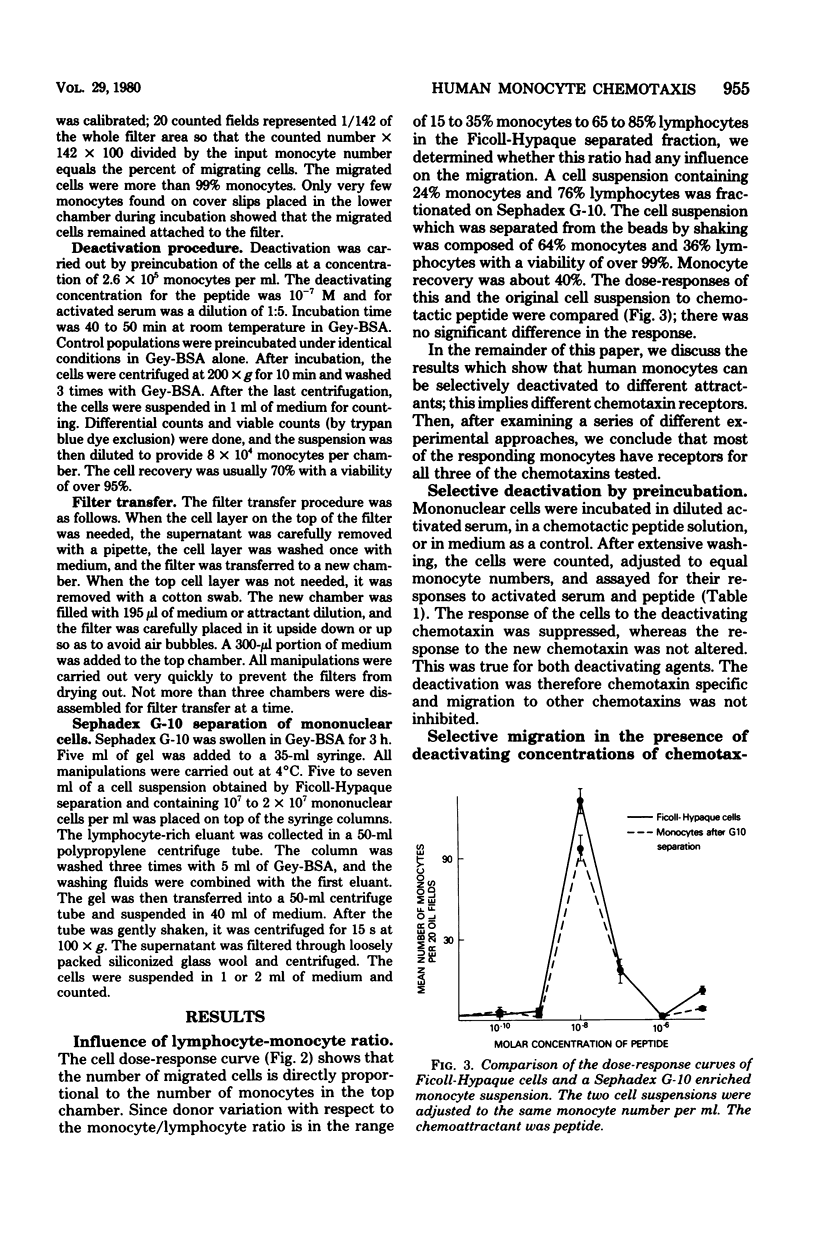
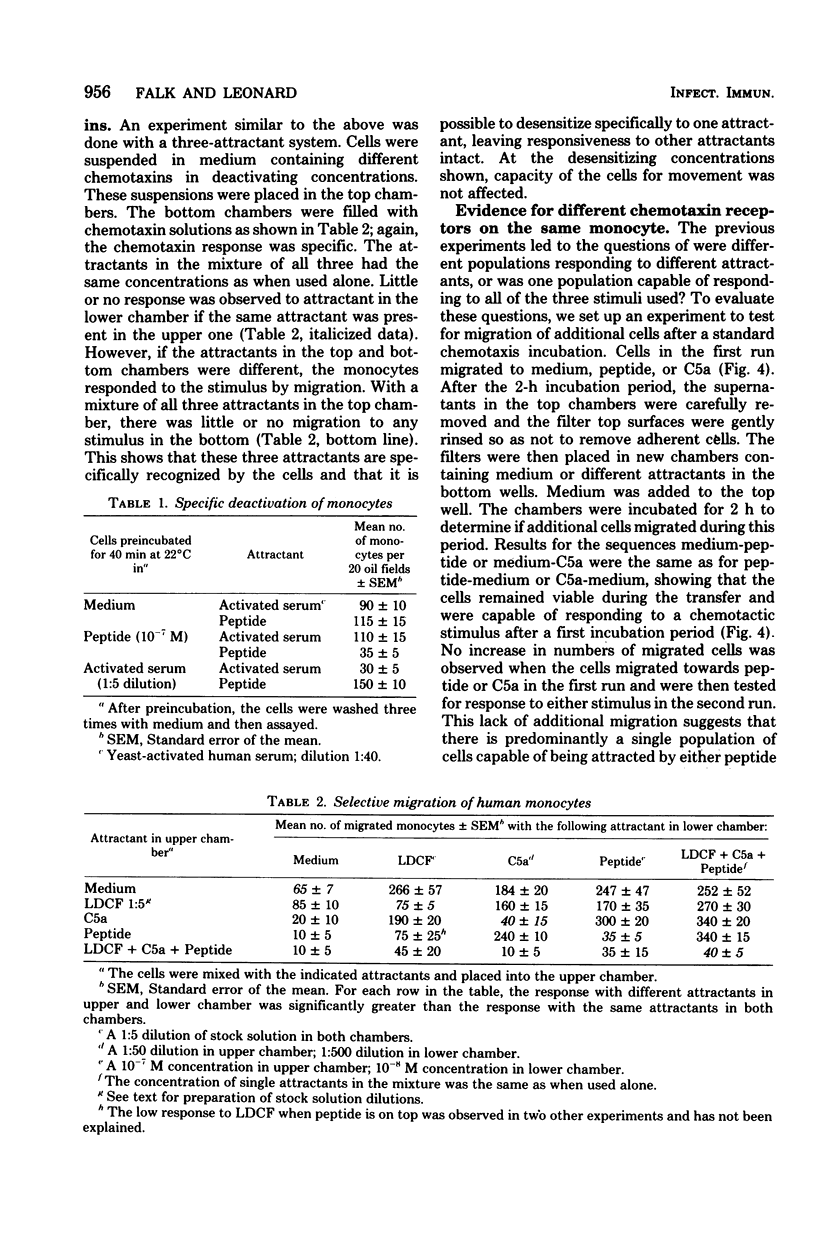
Only 20 to 40% of human blood monocytes were capable of responding to chemotaxins in vitro. This limit is not due to restrictions of the in vitro system, but is due to the existence of a migrating subpopulation. Over a wide range, the number of cells migrating toward a given concentration of chemotaxin was directly proportional to the number added to the chemotaxis chamber. These monocytes responded to all of the three stimuli used: human serum-derived C5a, human lymphocyte-derived chemotactic factor, and a synthetic peptide. It was possible to deactivate cells to one attractant, leaving the response to other attractants intact. This suggested that these attractants were recognized by different receptors. Several lines of evidence showed that most migrating cells had receptors for all three chemotaxins tested. Thus, if cells were assayed for migration to one attractant, no additional migration occurred when the remaining cells were assayed for migration to a different attractant. Furthermore, the same cells that had migrated toward one attractant were able to respond to other chemotaxins. We also found that a single attractant attracted as many cells as a combination of two or three attractants. Calculations from these data showed that at least 75% of the migrating monocytes have different receptors for all three attractants.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Furukawa C. T., Klebanoff S. J. Depressed mononuclear leukocyte chemotaxis in thermally injured patients. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman L. C., Snyderman R., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. A human mononuclear leukocyte chemotactic factor: characterization, specificity and kinetics of production by homologous leukocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Pert C. B., Morell J. L., Gross E. Antibiotics and peptides with agonist and antagonist chemotactic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):464–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90700-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. Role of a peptidase in phagocyte chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2439–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boetcher D. A., Leonard E. J. Abnormal monocyte chemotactic response in cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1091–1099. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Partial characterization of human C5a anaphylatoxin. I. Chemical description of the carbohydrate and polypeptide prtions of human C5a. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1688–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. P., Young A. L., Southard G. L. Methyl ester of N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine: chemotactic responses of human blood monocytes and inhibition of gold compounds. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jan-Feb;21(1):133–136. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J. A method for staining multiple chemotaxis filters. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Nov;9(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., McCormack R. T., Fiegel V. D., Simmons R. L. Chemotactic deactivation of human neutrophils: evidence for nonspecific and specific components. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):441–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.441-444.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Wilkinson S., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of 125I-chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10700–10706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Meadows L., Holder W., Wells S., Jr Abnormal monocyte chemotaxis in patients with breast cancer: evidence for a tumor-mediated effect. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Apr;60(4):737–740. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.4.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Territo M. C., Cline M. J. Monocyte function in man. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Whitmer D., Geotzl E. J., Austen K. F. Chemotactic deactivation of human eosinophils by the eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (38527). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jan;148(1):301–306. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


