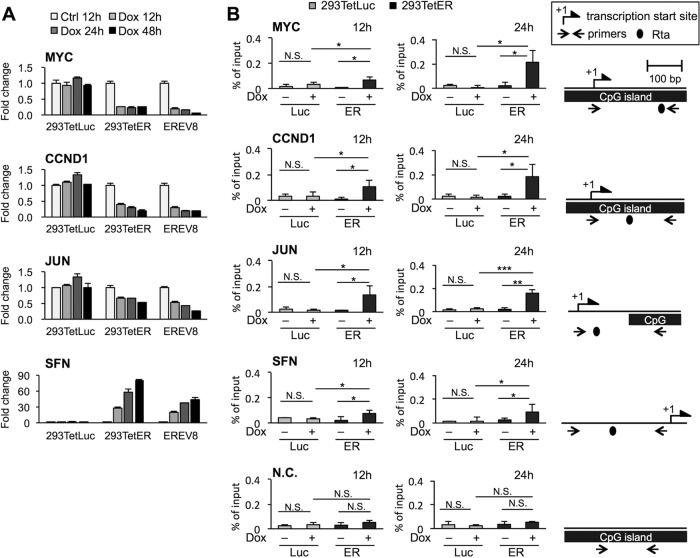
FIG 1.
EBV Rta-mediated gene repression is associated with Rta binding in promoters of target genes. (A) The levels of transcripts of MYC, CCND1, JUN, and SFN at the indicated time points in untreated (Ctrl) and doxycycline (Dox)-treated 293TetLuc, 293TetER, and EREV8 cells were measured by real-time RT-PCR assays. Data are presented as the means ± standard deviations (SD) from triplicate PCR results. Two independent experiments were performed; one representative data set is shown. (B) ChIP assays of EBV Rta in the cellular promoters of 293TetLuc (Luc) and 293TetER (ER) cells. Untreated (−) and Dox-treated (+) cells were harvested at the indicated time points and subjected to ChIP assays using specific antibodies against EBV Rta or normal rabbit IgG, which served as a control to exclude nonspecific binding (Fig. S1A). The eluted DNA fragments were quantified by real-time PCR analysis as a percentage of the input using the ΔCT method. The MYC gene body without Rta binding site served as a negative control (N.C.). Error bars depict the means ± SD from four independent experiments. Student's t test was used to evaluate the significant difference between the indicated data sets. ***, P < 0.005; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05; N.S., not significant. Schematic diagrams of transcription start sites, CpG islands, and potential Rta binding sites in the target promoter region are denoted on the right. Lengths of promoters are illustrated to scale.