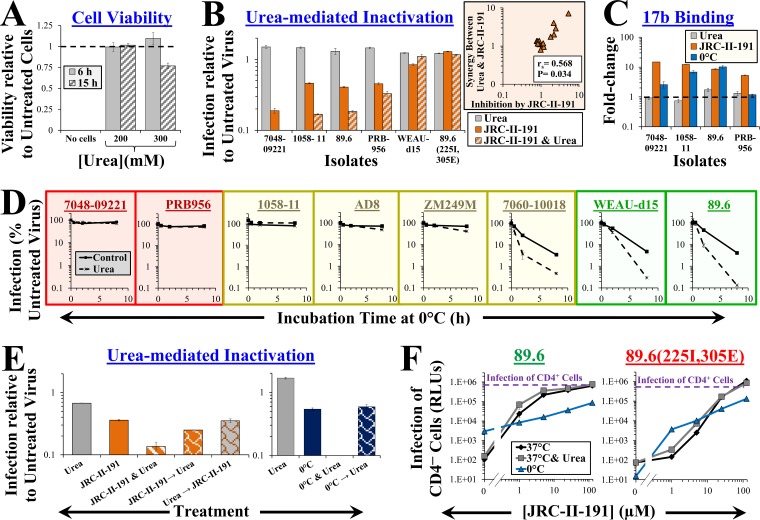
FIG 5.
Low concentrations of urea perturb the metastable states induced by cold and CD4Ms but not the native state of Env. (A) Effect of urea on viability of Cf2Th CD4+ CCR5+ cells measured using an ATP-based assay. The data are presented as fractions of viability in samples incubated without urea. (B) Effects of urea and JRC-II-191 on infectivity. Viruses containing the indicated Envs were added to cells in the presence of urea, JRC-II-191 (4 μM), or both for 6 h at 37°C. The cells were then washed and further incubated to measure residual infectivity. The inset shows a correlation between the JRC-II-191-mediated inhibition of each isolate and the synergy it exhibited for the combined use of urea and JRC-II-191. (C) Effects of urea, JRC-II-191, and cold on CoR-BS exposure. The data represent the fold change in binding of MAb 17b relative to samples incubated at 37°C without urea or JRC-II-191. The change in 17b binding induced after 1 h at 0°C is shown for comparison. (D) Urea enhances inactivation of cold-induced Envs. Viruses containing the indicated Envs were incubated at 0°C in the absence or presence of urea for 0.5, 2, or 8 h and then equilibrated to 37°C. Samples were subsequently added to cells and incubated for 6 h. The cells were then washed, and infectivity was measured 3 days later. The graphs are color coded by Env sensitivity to cold-induced structural changes (red, resistant; yellow, intermediate; green, sensitive). (E) Reversibility of the effects of JRC-II-191 and cold on urea-mediated inactivation. Viruses containing 89.6 Env were exposed to 0°C or JRC-II-191 (4 μM) in the absence or presence of urea for 2 h. To test reversibility, the viruses were first exposed to 0°C or JRC-II-191 for 2 h, followed by removal of the treatment and incubation with urea for 2 h. As controls, some samples were treated with urea prior to addition of JRC-II-191. (F) Effect of urea or cold on JRC-II-191-induced infection of CD4− CCR5+ cells. Viruses were spinoculated onto CD4− CCR5+ cells at 10°C and then incubated for 2 h at 37°C or 0°C in the absence or presence of urea and JRC-II-191. The cells were then equilibrated to 37°C and washed, and infectivity was measured 3 days later. Data that describe infection at 37°C are also shown in Fig. 4E. The dashed lines represent infectivity measured in the same experiment by untreated virus bound to CD4+ CCR5+ cells. The error bars indicate SEM.