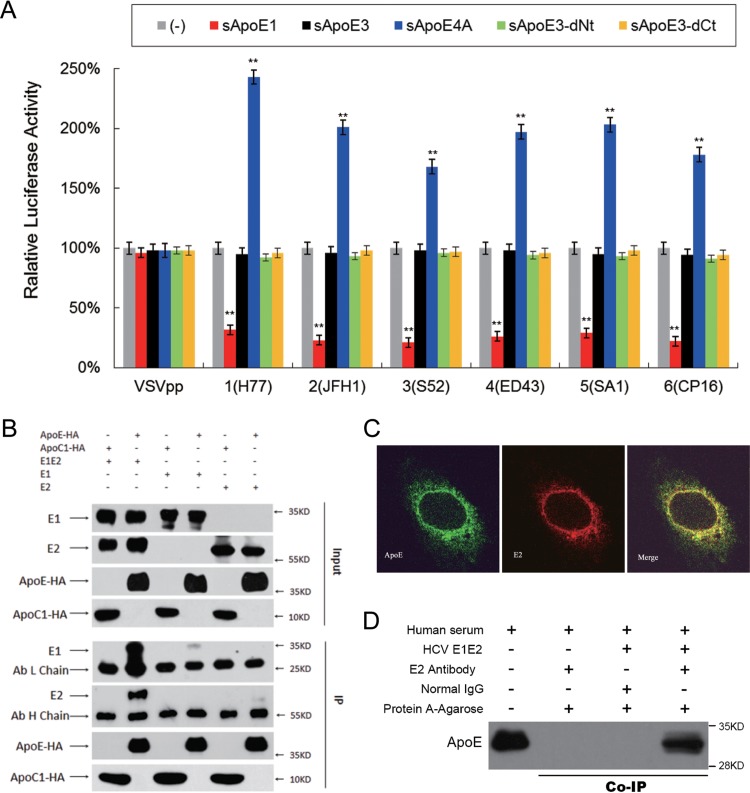
FIG 6.
Interactions between recombinant HCV envelope proteins and sApoE. (A) The infectivity of pseudoviral particles influenced by sApoE variants depends on HCV envelope proteins. The HCV or VSV envelope protein pseudotyped lentiviral particles containing a luciferase reporter gene were produced and incubated with cell culture supernatant containing different sApoE variants or mutants secreted from 293T cells at room temperature for 30 min and subsequently used to infect Huh7.5 cells in a 24-well culture plate. At 5 h.p.i., the mixture was removed, and the cells were washed twice with PBS and then incubated with DMEM containing 10% FBS. After 24 h, the cells were lysed for luciferase assays. The quantitative results derived from the data were converted to percentages of the control in the bar graph, and the data are shown as the means ± SDs (error bars) pooled from three independent experiments. **, P < 0.01 (unpaired Student's t test). (B) Interactions between sApoE and HCV envelope proteins were analyzed by coimmunoprecipitation. 293T cells stably expressing the HCV envelope protein E1E2, E1, or E2 were lysed and separately incubated with cell culture supernatant containing sApoE3-HA or sApoC-HA secreted by 293T cells. These mixtures were then captured by HA-specific immunoprecipitation. The proteins (input) or immunocomplexes (IP) in the mixture were analyzed by Western blotting. Proteins are specified on the left, and molecular mass standards are labeled on the right. (C) Colocalization of HCV envelope proteins and cApoE in hepatocytes. Recombinant HCV envelope proteins were expressed in Huh7.5 cells. cApoE (green) and HCV E2 (red) proteins were analyzed by immunofluorescence with specific antibodies and observed via confocal microscopy. (D) Co-IP of recombinant HCV envelope proteins with sApoE in human serum. Lysates from naive 293T cells or cells stably expressing HCV envelope proteins (E1E2) were incubated with human serum and protein G-conjugated agarose beads (Invitrogen) bound with normal mouse IgG or an E2-specific MAb. Upon extensive washing, precipitated proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and then transferred onto a PVDF membrane. ApoE protein was subsequently detected by Western blotting using an ApoE-specific MAb.