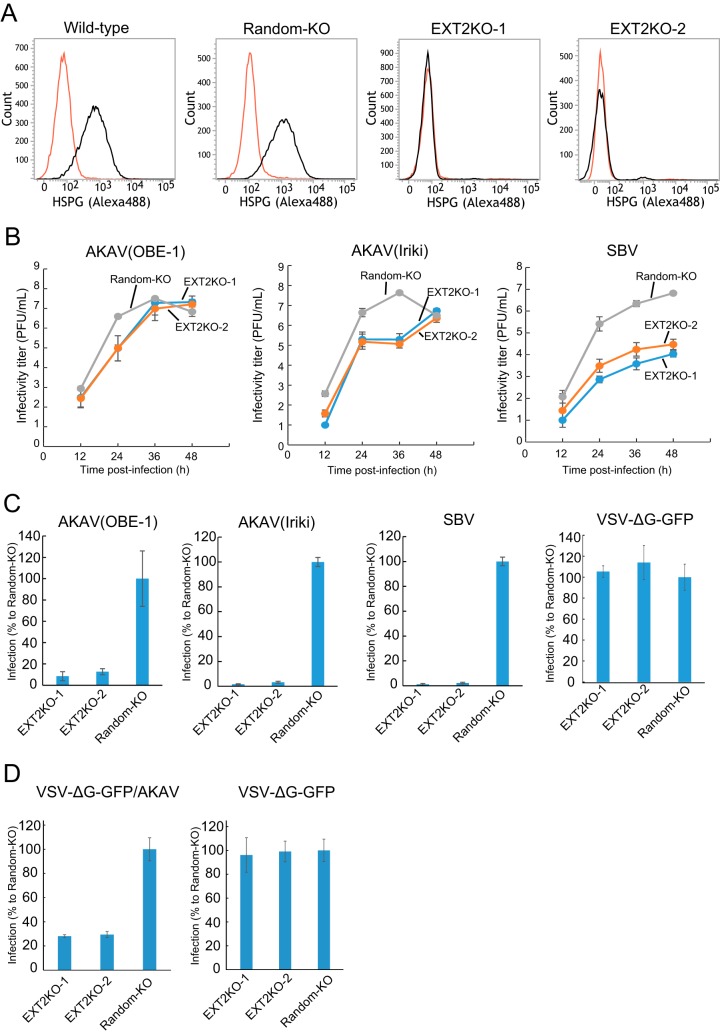
FIG 2.
AKAV and SBV growth kinetics and infectivity in HSPG-KO HmLu-1 cells. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of EXT2-KO HmLu-1 cells. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated EXT2-KO cell clones (EXT2-1 and EXT2-2) were labeled with anti-heparan sulfate mouse monoclonal antibody (10E4) (black) or with isotype control (red) and analyzed by flow cytometry (FACSVerse; BD Biosciences). Representative data (one out of three clones of random-KO, EXT2KO-1, and EXT2KO-2) are shown. (B) Growth kinetics of AKAV or SBV in HSPG-KO cells. AKAV(OBE-1), AKAV(Iriki), or SBV was inoculated onto three clones of random-KO, EXT2KO-1, and EXT2KO-2 cells at a multiplicity of infection of 0.01. Virus titers were determined by plaque assay in normal HmLu-1 cells. The data are reported as the mean titer for three clones of each KO cell (EXT2KO-1, EXT2KO-2, or random-KO) with standard deviations. (C) Infectivities of AKAV and SBV in HSPG-KO cells. Random-KO or HSPG-KO cells were infected with AKAV(OBE-1), AKAV(Iriki), SBV, or control VSV-ΔG-GFP. Cells were stained for AKAV or SBV antigen, and positive cells were counted under a fluorescence microscope. For VSV-ΔG-GFP-infected cells, GFP-positive cells were counted under a fluorescence microscope. Results are expressed as percentages relative to the number of positive random-KO cells. The data are reported as the mean value for three clones of each KO cell (EXT2KO-1, EXT2KO-2, or random-KO) with standard deviations. (D) Infectivities of VSV pseudotyped with AKAV Gn/Gc (VSV-ΔG-GFP/AKAV) in HSPG-KO cells. Random-KO or HSPG-KO cells were infected with VSV-ΔG-GFP/AKAV or control VSV-ΔG-GFP. GFP-positive cells were counted under a fluorescence microscope. Results are represented as percentages relative to the number of positive random-KO cells. The data are shown as the mean value for three clones of each KO cell (EXT2KO-1, EXT2KO-2, or random-KO) with standard deviations.