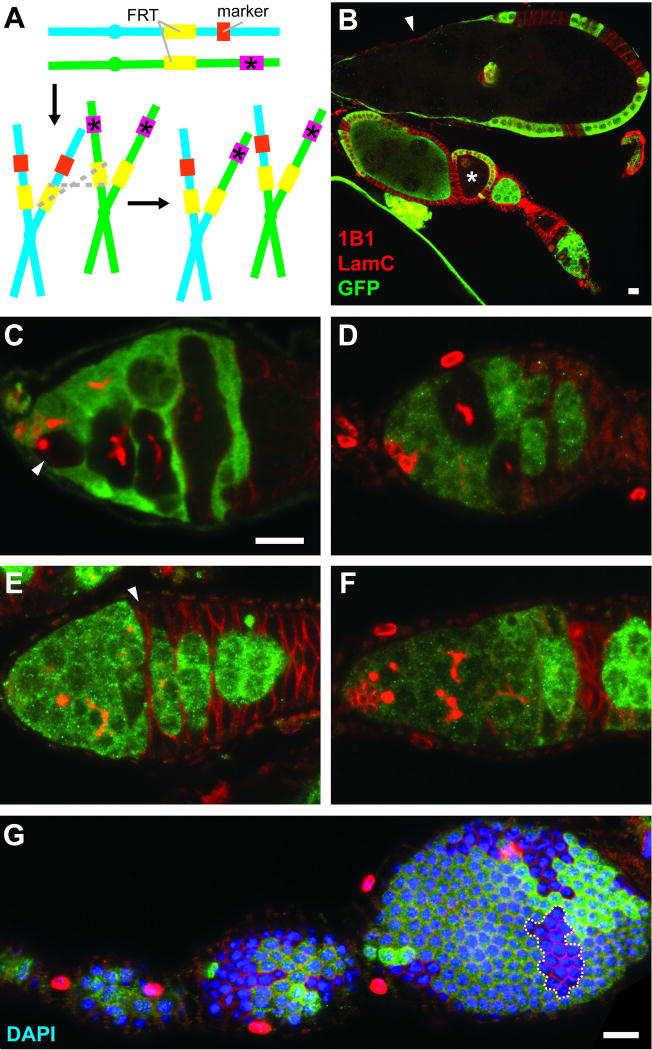
Fig. 1.
Confocal images of genetic mosaic ovarioles and germaria. (A) GFP- or β-gal-negative mutant cells can be generated as unequal sister chromatids, produced as a result of FLP/FRT-mediated mitotic recombination (grey dashed lines), segregate during mitosis. Mutant allele is indicated by pink box and asterisk. Marker (orange box) is a constitutively expressed transgene encoding GFP or β-gal. (B) Mosaic ovariole containing previtellogenic (asterisk) and vitellogenic (arrowhead) follicles with GFP-negative germline cysts. (C) In a mosaic germarium, a GFP-negative GSC (arrowhead) gives rise to GFP-negative progeny. (D) A GSC loss event. GFP-negative germline cysts are present, but the original GFP-negative GSC is absent. (E) The FSC is located immediately anterior to the 2a/2b border, and it is recognizable as the anterior-most cell (arrowhead) in a GFP-negative follicle cell clone. (In region 2a, individual 16-cell cysts do not fill entire diameter of germarium, whereas in region 2B, lens-shaped 16-cell cysts span the breadth of germarium.) (F) When the FSC is lost, GFP-negative follicle cells can be detected, but the most anterior follicle cells are far posterior to 2a/2b. (G) A transient clone (dashed line) in a follicle cell monolayer provides an indirect readout for follicle cell proliferation. Absence of GFP (green) indicates marker-negative cells; 1B1 (red) labels fusomes and follicle cell membranes; Lamin C (LamC, red) labels cap cell nuclear envelopes; DAPI (blue) labels nuclei. Scale bars represent 10 µM. Images in (C–F) are shown at the same magnification.