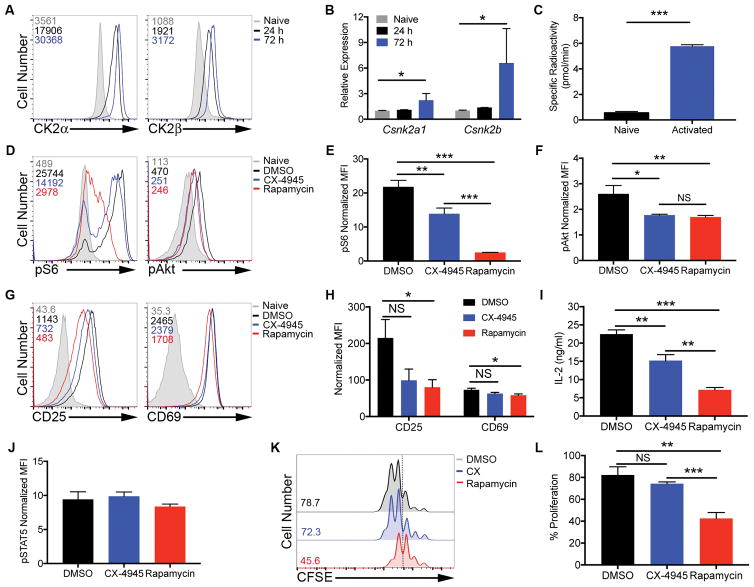
Figure 1. CK2 Kinase Activity is Induced Upon CD4+ T Cell Activation and Promote Akt/mTOR Signaling, but is Not Required for Activation or Proliferation.
(A, B) CD4+ T cells were activated with plate-bound anti-CD3 (10 μg/ml) and soluble anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml) antibodies. (A) At 24 and 72 h, cells were stained for intracellular CK2α and CK2β; numbers represent corresponding mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs), and data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) RNA was extracted and qPCR performed using primers for Csnk2a1 and Csnk2b (n=3). (C) At 72 h, naïve and activated cells were assayed for CK2 kinase activity. Data represent mean of 2 technical replicates, and are representative of 3 independent experiments. (D–J) Naïve CD4+ T cells were activated in the absence or presence of CX-4945 (2 μM) or rapamycin (100 nM) for 24 h. (D–F) Cells were stained for phosphorylated S235/236 S6 kinase and phosphorylated S473 Akt. (D) Representative histograms and (E, F) MFIs normalized to the corresponding naïve control +/− SEM are shown (n=3). (G–I) Cells were stained for surface expression of the activation markers CD25 and CD69. (G) Representative histograms and (H) MFIs normalized to the corresponding naïve control +/− SEM are shown (n=3). (I) IL-2 was detected in the supernatant by ELISA. Concentrations +/− SEM are shown (n=3). (J) Cells were stained for phosphorylated Y694 STAT5. MFIs normalized to the corresponding naïve control +/− SEM are shown (n=3). (K, L) Naïve CD4+ T cells were incubated with CFSE dye and activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies in the absence or presence of CX-4945 or rapamycin for 72 h, and proliferation assessed by CFSE dilution. (K) Representative histograms and (L) frequencies of cells undergoing 3 or more divisions +/− SEM (n=3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.