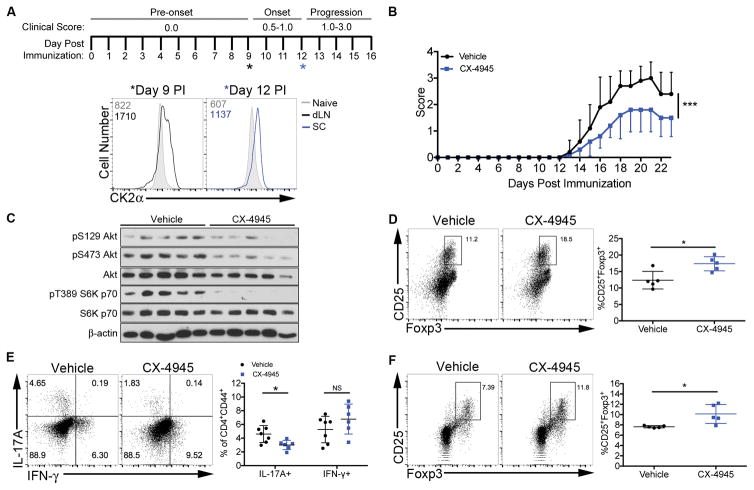
Figure 5. In Vivo CX-4945 Pre-treatment Suppresses Th17 Cell Differentiation and Promotes Tregs During EAE.
(A) A schematic of disease induction, scoring and progression is shown with asterisks indicating time-points for CK2α detection. At days 9 and 12 post immunization (PI), cells were enriched from the draining lymph nodes (dLN) and spinal cord, respectively, and stained for intracellular CK2α. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. (B–D) Mice were treated with CX-4945 (20 mg/kg/day) or sodium phosphate buffer (Vehicle) from 7 days before immunization throughout disease. Data are from 1 representative experiment of at least 2 independent experiments. (B) Clinical scores from days 0 to 23 PI are show; n=5/group. (C) On day 9, CD4+ T cells were enriched from the spleens via magnetic selection, lysed and immunoblotted for phosphorylated S129 and S473 Akt and T389 and S371 S6K p70; n=5/group. (D) On day 23, mononuclear cells were enriched from the spinal cord and Tregs identified by CD25 and Foxp3 staining; n=5/group. (E, F) Mice were treated with vehicle or CX-4945 (20 mg/kg/day) via oral gavage from days 0 to 7 PI. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. (E) At day 7, CD4+ T cells from the dLNs were stained for IL-17A and IFN-γ; n=8/group. (F) At day 7, CD4+ T cells from the spleens were stained for CD25 and Foxp3; n=5/group. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.