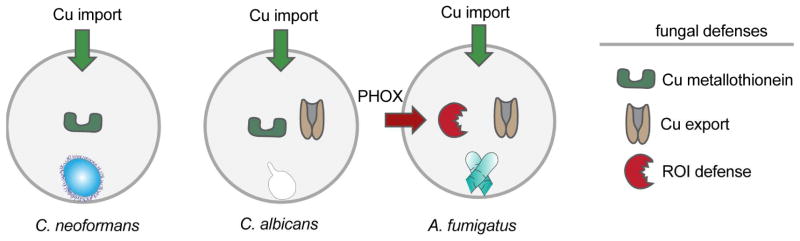
Fig. 6. Copper-defense strategies of the three fungal pathogens C. neoformans, C. albicans and A. fumigatus.
Upon infection, all depicted pathogens activate host copper importers (Ctr1 and ATP7A). Known fungal defense strategies include metallothioneins in C. neoformans and metallothioneins and a copper-exporter in C. albicans. Our results demonstrate that in A. fumigatus the copper-exporter and not the copper-metallothionein is involved in copper-defense. Furthermore, we demonstrate that host PHOX generated ROI is potentiated in strains unable to export copper and that copper-export and ROI-detoxification can remediate virulence of the A. fumigatus ΔaceA mutant. We hypothesize that the existing ROI-detoxification mechanisms of C. neoformans and C. albicans may also be important in copper-regulon interactions of these yeast with host phagocytes in a manner similar to A. fumigatus.