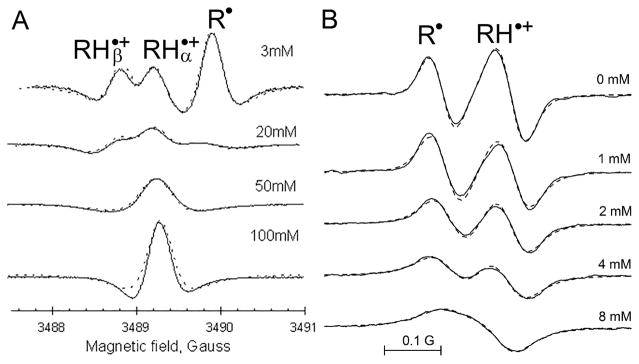
Figure 4.
(A) Second-derivative of high-field component of X-band EPR spectra of aqueous 0.3 mM solutions of the radical NR4 (pKR = 6.1) measured at various phosphate buffer concentrations, pH = 5.9 and temperature, 23 °C. At low phosphate concentration (top spectrum), the narrow lines of this deuterated probe allows for distinguishing not only R• and RH•+ and forms but also discriminating two protonated radical forms with different nuclear spin projection of attached proton, and . The fitting calculated spectra (dotted lines) to the experimental ones performed as described in ref 57 provides the values of the rate constants of proton exchange of the NR4 with phosphate, k7(NR4) = 2.6 × 108 M−1 s−1, k−7 (NR4) = 1.6 × 109 M−1 s−1. Reproduced from ref 57 with permission of Springer. Copyright 2001 Springer. (B) High-field component of the L-band EPR spectra of aqueous 0.2 mM solutions of the pTAM radical (pkR = 6.9) measured at various phosphate buffer concentrations, pH 6.8, under anoxic conditions and temperature 37 °C. The fitting calculated spectra (dotted lines) to the experimental ones performed as described in ref 29 provides the values of the rate constants of proton exchange of the pTAM with phosphate, k7(pTAM) = 2.1 × 107 M−1 s−1, k−7(pTAM) = 3.3 × 107 M−1 s−1. Reproduced from ref 28. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society.