Figure 6.
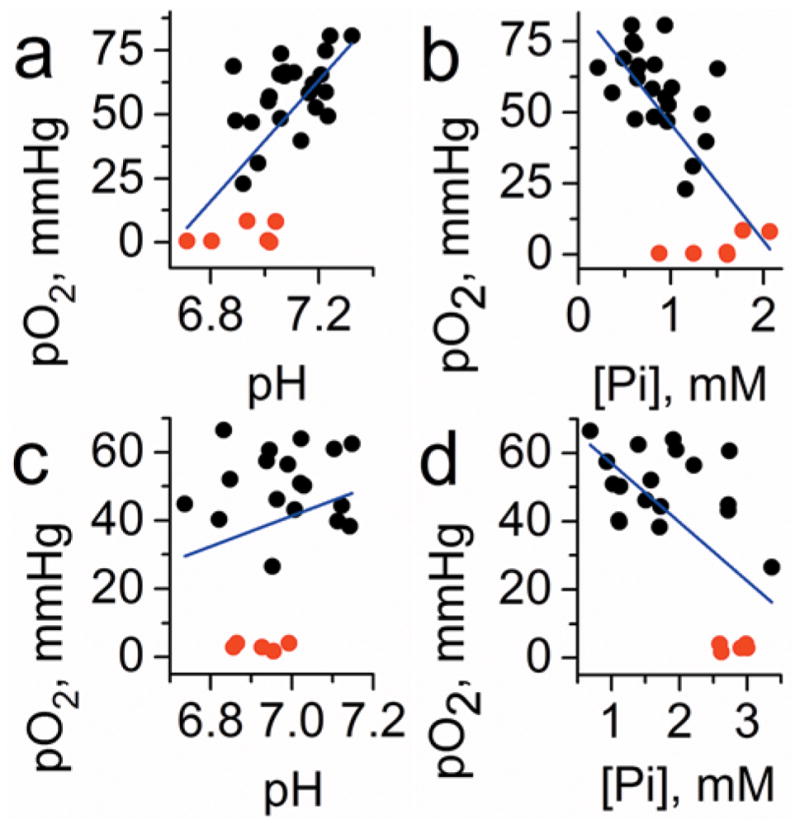
Correlation between interstitial pO2, pHe, and Pi values measured in normal mammary glands of FVB/N wild type mice and in the TME of breast cancer in MMTV-PyMT transgenic mice (n = 23). To extend the range of oxygen variations, anoxic conditions in interstitial space were established by i.t. injection of oxygen-consuming enzymatic system of glucose/glucose oxidase (red symbols). Blue lines represent linear fit for the total data sets. (a) A positive correlation between pO2 and pHe in normal tissue (r = 0.5, p = 0.014 for black symbols; r = 0.64, p = 1.8 × 10−4 for total data set) vs (c) no significant correlation between pO2 and pHe in TME (r = 0.01, p = 0.97 for black symbols; r = 0.23, p = 0.3 for total data set) were found. A negative correlations between pO2 and Pi both in (b) normal tissue (r = −0.51, p = 0.013 for black symbols; r = −0.7, p = 2.3 × 10−5 for total data set), and (d) in TME (b, bottom: r = −0.4, p = 0.079 for black symbols; r = −0.62, p = 0.001 for total data set) were found. Adapted from ref 71 with permission. Copyright 2017 Springer Nature.
