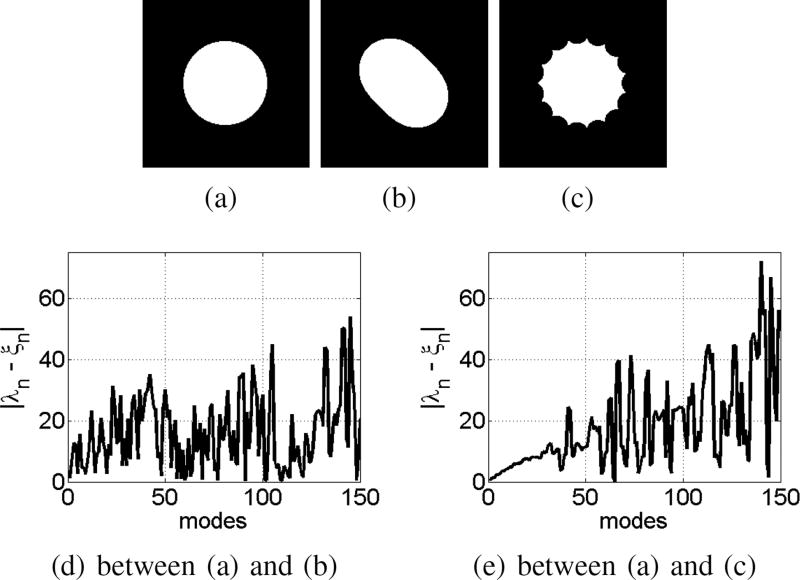
Fig. 2.
Multi-scale characteristics of different spectral modes:(a), (b) and (c) show three synthetic shapes. In (d) we plot the absolute differences between the corresponding modes of (a) and (b) with respect to the spectral index. In (e) we plot the same difference for the shapes in (a) and (c). The shape difference between (a) and (b), which is at a coarser level, is already captured at the lower spectral modes. The difference between (a) and (c) results in lower differences in lower spectral modes because these objects are more similar at a coarser level. At the higher spectral modes though, the difference between (a) and (c) becomes more prominent since these objects differ more substantially at the finer scales. The plots in (d) and (e) demonstrate that the higher modes for a given object are more important for finer scale shape details.