Figure 5.
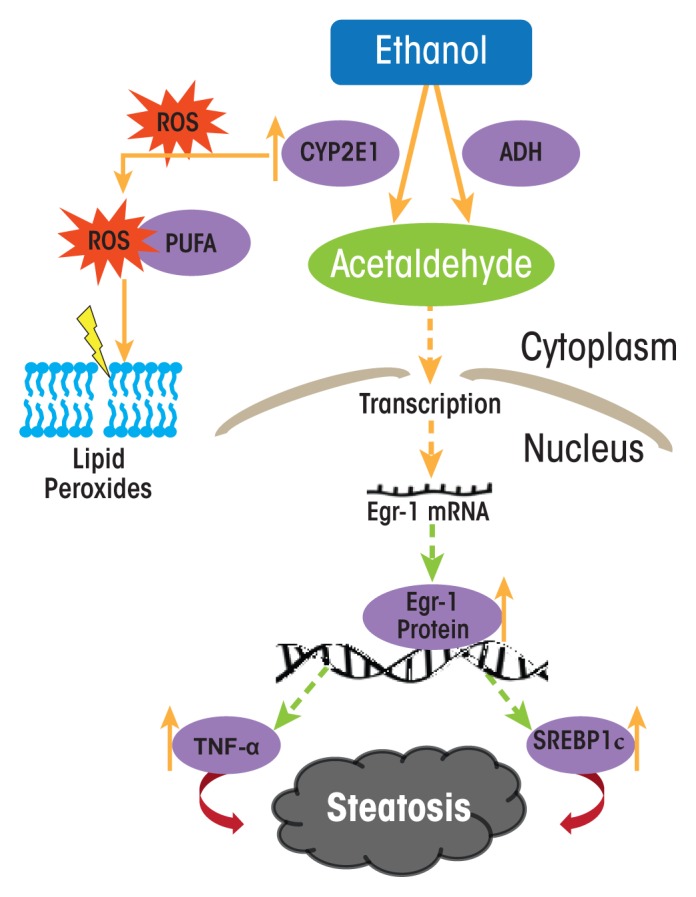
Proposed mechanism by which ethanol oxidation regulates early growth response-1 (Egr-1) and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) to enhance lipogenesis. Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) each catalyze ethanol oxidation, producing acetaldehyde. This aldehyde enhances Egr-1 gene transcription by activating the Egr-1 promoter, thereby increasing the levels of Egr-1 mRNA and, subsequently, nuclear Egr-1 protein. It is believed that nuclear Egr-1 protein regulates transcription of SREBP-1c and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) genes to initiate ethanol-induced lipogenesis and fatty liver (i.e., steatosis).
NOTE: PUFA = polyunsaturated fatty acid; ROS = reactive oxygen species.
SOURCE: Figure adapted from Thomes et al. 2013.
