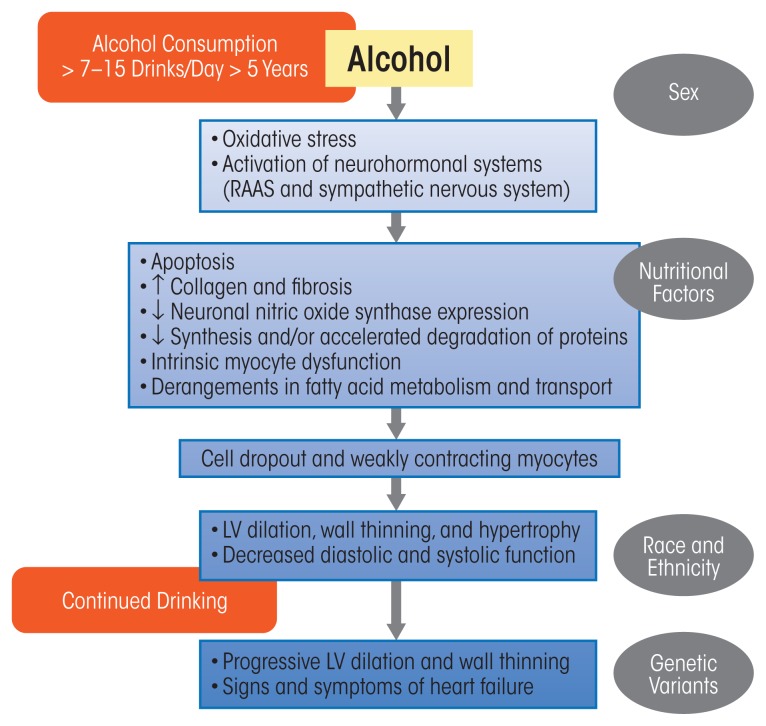
Figure 4.
Pathophysiologic schema for the development of alcoholic cardiomyopathy (ACM). As noted in the text, the exact amount and duration of alcohol consumption that results in ACM in human beings varies. The exact sequence of the development of ACM remains incompletely understood. Data from animal models and human beings with a history of long-term drinking suggest that oxidative stress may be an early and initiating mechanism. Many cellular events, such as intrinsic myocyte dysfunction, characterized by changes in calcium homeostasis and regulation and decreased myofilament sensitivity, can come about due to oxidative stress. Variables in gray ovals represent potential mediating factors.
NOTE: LV = left ventricle, RAAS = renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system.
SOURCE: Adapted from Piano and Phillips 2014.