Figure 8.
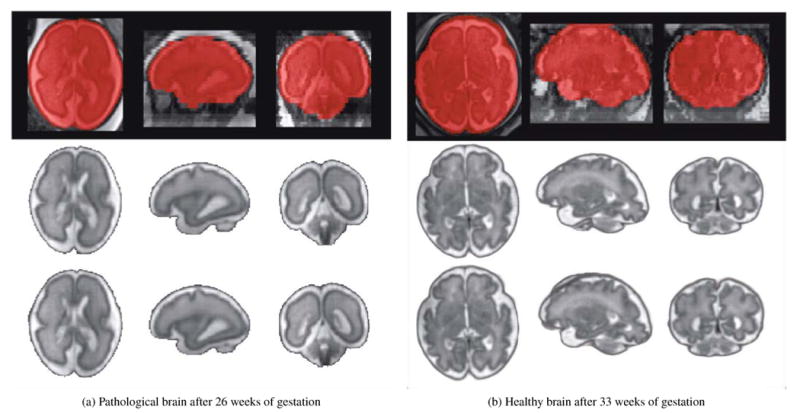
Brain extraction and reconstruction results of one pathological brain diagnosed with unilateral ventriculomegaly (Case P3) and one healthy brain (Case F12). An overlay of the original low-resolution image with the final brain mask automatically extracted is shown in the first row. The reconstruction results obtained using the brain masks manually drawn and the brain masks automatically extracted are shown in the second and third row respectively. Case P3 illustrates one case where the expert observers judged both reconstructed images having the same quality. Case F12 illustrates one case where the expert observers preferred the image reconstructed using manual brain masks as a small region outside the brain was included in the fully automated reconstruction. These results showed that using the proposed brain localization and extraction methods allowed us to obtain fully automatic high-quality reconstructions, where the brain is conventionally oriented, without any further effort.
