Figure 6.
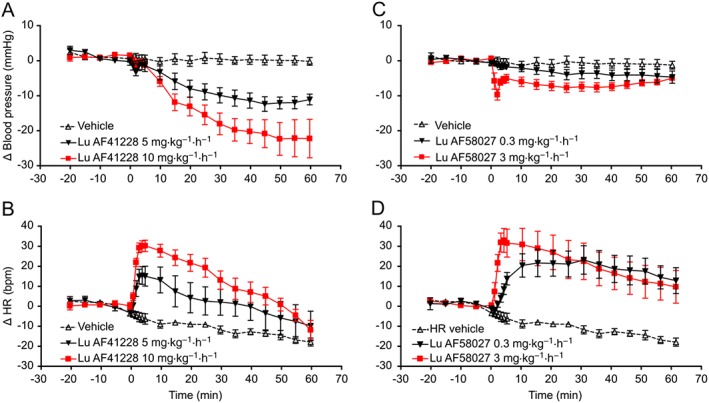
BP decrease and HR increase in response to PDE1 inhibition in anaesthetized rats. After equilibrium was reached, baseline was recorded for 20 min and animals were then given i.v. infusions of either compound or vehicle (continuous infusion over 60 min). Plasma exposure was measured in separate time‐matched animals. (A) Decrease in BP in response to Lu AF41228 (5 and 10 mg·kg−1·h−1). A minor response occurred immediately after start of the drug infusion at both doses followed by a return towards baseline after 5 min. BP then dose‐dependently decreased compared with vehicle throughout the experiment (5 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 4, 10 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 6, vehicle: n = 4). (B) Dose‐dependent increase in HR in response to Lu AF41228 (5 and 10 mg·kg−1·h−1). Response occurred immediately after start of the drug infusion (5 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 4, 10 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 6, vehicle: n = 4). (C) Decrease in BP in response to Lu AF58027 (0.3 and 3 mg·kg−1·h−1). Only a small but significant decrease was observed at 0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1. At 3 mg·kg−1·h−1, a minor response occurred immediately after start of the drug infusion followed by a return towards baseline after 5 min. BP then remained stably decreased compared with vehicle throughout the experiment (0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 4, 3 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 6, vehicle: n = 4). (D) Dose‐dependent increase in HR in response to Lu AF58027 (0.3 and 3 mg·kg−1·h−1). Response occurred immediately after start of the drug infusion (0.3 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 4, 3 mg·kg−1·h−1: P < 0.05, n = 6, vehicle: n = 4).
