Figure 3.
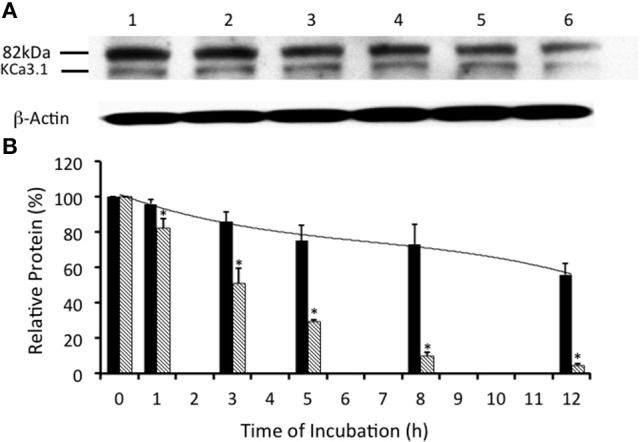
Effects of E1-ubiquitin activating enzyme inhibition via UBEI-41 on the expression of streptavidin labeled KCa3.1-BLAP channels. (A) After basolateral streptavidin labeling of KCa3.1 channels, cells were further incubated in 37°C for 0 (no incubation), 1, 3, 5, 8, or 12 h with UBEI-41 (50 μM) before being lysed and detection of KCa3.1 by immunoblot. Lane 1: Control no incubation (t = 0), Lane 2: 1 h of incubation (t = 1), Lane 3: 3 h of incubation (t = 3), Lane 4: 5 h of incubation (t = 5), Lane 5: 8 h of incubation (t = 8), and Lane 6: 12 h of incubation (t = 12). Each lane was loaded with 30 μg of protein and β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) Relative expression levels of KCa3.1 in the presence of UBEI-41 (black bars). Relative expression levels of KCa3.1 (serving as control data) from Figure 2 were plotted (hatched bars). Relative protein expression demonstrated that the expression level of KCa3.1 (control, 0 h, black bar) remained the same after 1 h of treatment of UBE-41, but was higher than the 1 h control non-treated cells (hatched bars). Also, by 3 h only ~10% of the labeled channel had been degraded compared with the 0 h control, however, at 3 h, the non-treated cells exhibited degradation of ~50% of the labeled KCa3.1 (hatched bar) (*P ≤ 0.05, n = 4). Thus, UBEI-41 effectively slowed the degradation of KCa3.l, extending the channel half-life to more than 12 h compared to non-treated control cells (~3 h).
