FIGURE 1.
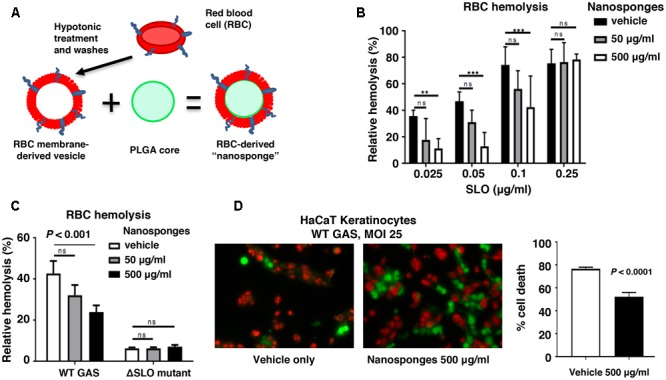
RBC nanosponges decrease GAS SLO-induced hemolysis and keratinocyte cytotoxicity. (A) Schematic showing fusion of RBC-derived ghost membrane vesicle and PLGA core to create nanosponge therapeutic. Human whole blood was centrifuged and washed with PBS + 1% EDTA to purify RBCs, then subjected to hypotonic treatment and centrifugation to rupture the membrane and remove intracellular content. PLGA cores were prepared from a 0.67 dL/g carboxy-terminated PLGA polymer by solvent displacement and resulting nanoparticles fused with RBC membranes by sonication. (B) RBC nanosponges inhibit purified SLO-induced RBC in a dose-dependent manner. (C) RBC nanosponges inhibit hemolysis induced by SLO produced by live WT GAS bacteria; isogenic SLO-deficient mutant serves as control. (D) Coincubation with RBC nanosponges increases survival of HaCaT keratinocytes infected with WT GAS at MOI = 25 bacteria/cell; live/dead cell staining illustrates viable (green) or dead (red) cells. Results are from experiments performed in triplicate, and reported as mean ± SEM from at least three experiments.
