Figure 1.
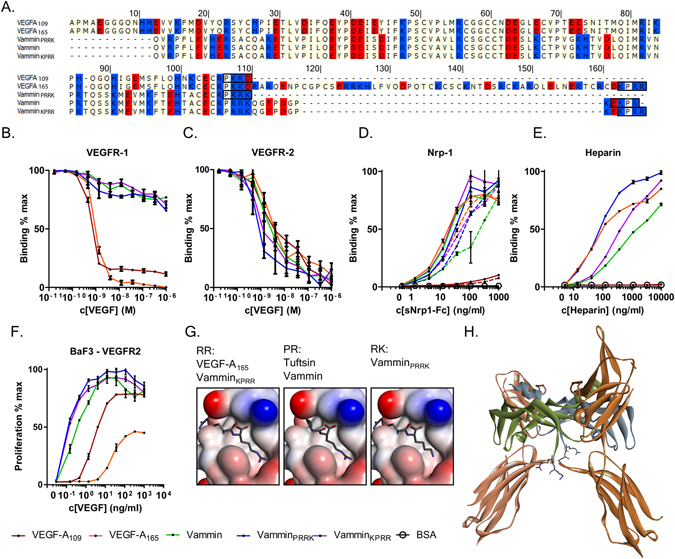
(A) Sequence alignment of recombinant VEGF-A and Vammin proteins. Basic amino acids are in blue and acidic in red background. The last four amino acids expected to be important for NRP-1 binding are in black boxes. (B) VEGFR-1 competition binding assay (C) VEGFR-2 competition binding assay (D) NRP-1 binding into VEGF coated plates the presence of heparin (solid lines) and without heparin (dotted lines) (E) Heparin binding in VEGF coated plates (F). BaF3-VEGFR-2 proliferation assay. In B to F the values are expressed as mean ± SD. (G) Binding of the two C-terminal amino acids into the NRP-1 binding pocket. RR and PR sequences are drawn based on VEGF-A165/NRP-1 and Tuftsin/NRP-1 complex structures. (PDB IDs 4DEQ and 2ORZ). RK sequence is modeled based on VEGF-A165/NRP-1 complex structure. Ligand amino acids are shown as sticks and NRP-1 as surface rendering colored by interpolated charge. (H) A model of location of the VamminPRRK C-terminus. Vammin crystal structure (PDB ID 1 WQ8) was superimposed onto VEGF-C/VEGFR-2 complex crystal structure (PDB ID 2X1W). The two VEGFR-2 monomers are seen with the brown colors and the two antiparallel dimer forming Vammin chains with green and blue. The C-terminal Arg97 and Lys98 of Vammin projecting outward from the complex are shown as sticks.
