Figure 3.
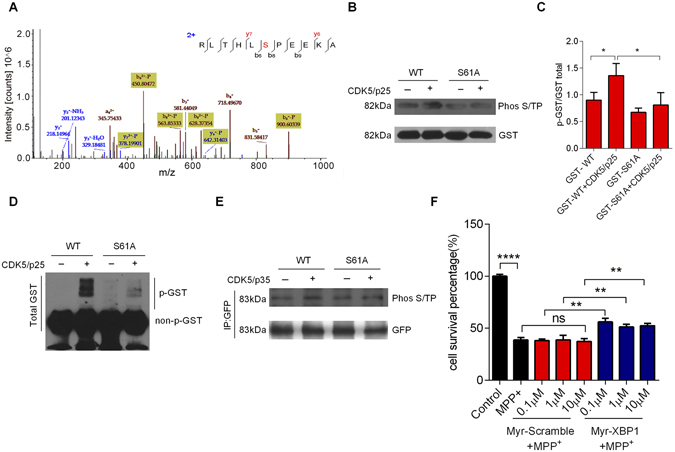
CDK5 phosphorylates XBP1s at Ser61. (A) Mass spectrometry showed that CDK5 phosphorylated XBP1s at Ser61. The peptide RLTHLSPEEKA, which contained the XBP1s Ser61 residue, was synthesized in vitro. (B) CDK5/p25 phosphorylated XBP1s at Ser61 in an in vitro kinase assay. Purified glutathione-S-transferase (GST)-XBP1s WT or S61A fusion proteins were mixed with active CDK5/p25, and the phosphorylation signal was analyzed using a Phos S/T antibody. (C) Statistical analysis of the expression of phosphorylated GST-XBP1s WT or S61A fusion proteins. (D) The phosphorylation signal of GST-XBP1s WT or S61A fusion proteins was analyzed by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE gels. (E) CDK5/p35 phosphorylated XBP1s at Ser61 in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with HA-CDK5/Myc-p35 and GFP-XBP1s-WT or GFP-XBP1s-S61A plasmids, and then collected and immunoprecipitated with a Phos S/T antibody 24 h after transfection. (F) The transmembrane peptide Myr-XBP1, which contained the XBP1s Ser61 residue, had a protective effect on MPP+-induced cell death. Primary cultured neurons were pretreated with XBP1 peptide or scrambled peptide (0.1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM, 30 min), and then treated with MPP+ (250 μM, 24 h). Cell survival was visualized by MTT assay. Data are mean ± s.d. of n = 3 independent experiments. Significance was determined by unpaired Student’s t test (C and F). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.
