Figure 2.
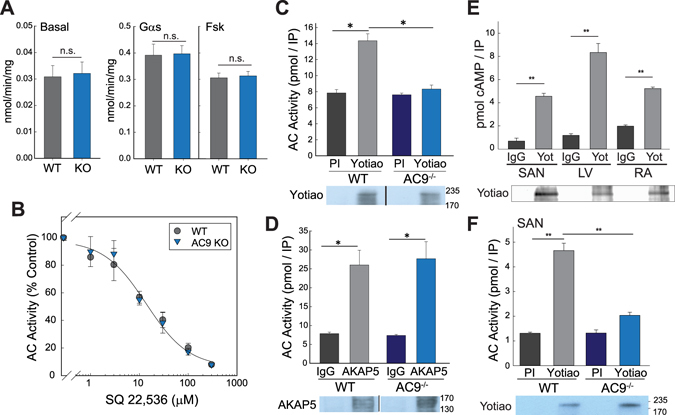
AC9 activity and AKAP association in heart. (A,B) Membranes were prepared from 6 wk WT versus AC9−/− heart. (A) AC activity was measured under basal conditions and upon stimulation with 300 nM Gαs or 50 µM forskolin (n = 4, performed in duplicate or triplicate). (B) AC activity was measured in the presence of increasing concentrations of SQ22,536 in the presence of 300 nM Gαs (n = 3, performed in duplicate). (C,D) Heart extracts from WT or AC9−/− mice were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with pre-immune (control) or anti-Yotiao (C) and control IgG or anti-AKAP5 (D). AKAP-associated AC activity was stimulated with 300 nM Gαs and measured (n = 3–4). Data are shown as mean +/− SD. A portion of the IP’s from (C and D) were subjected to WB analysis for the appropriate AKAP. (E) Yotiao-associated AC activity was measured from WT sinoatrial node (SAN), left ventricle (LV), and right atrium (RA) tissue homogenates as in panel (C). Immunoblot of Yotiao from IPs is shown below. (F) Yotiao-associated activity from WT and AC9−/− SAN as measured in panel (C); Yotiao immunoblot is shown below (n = 3). Full-length WBs are presented in Supplementary Fig. S6.
