Abstract
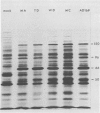
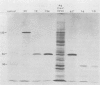
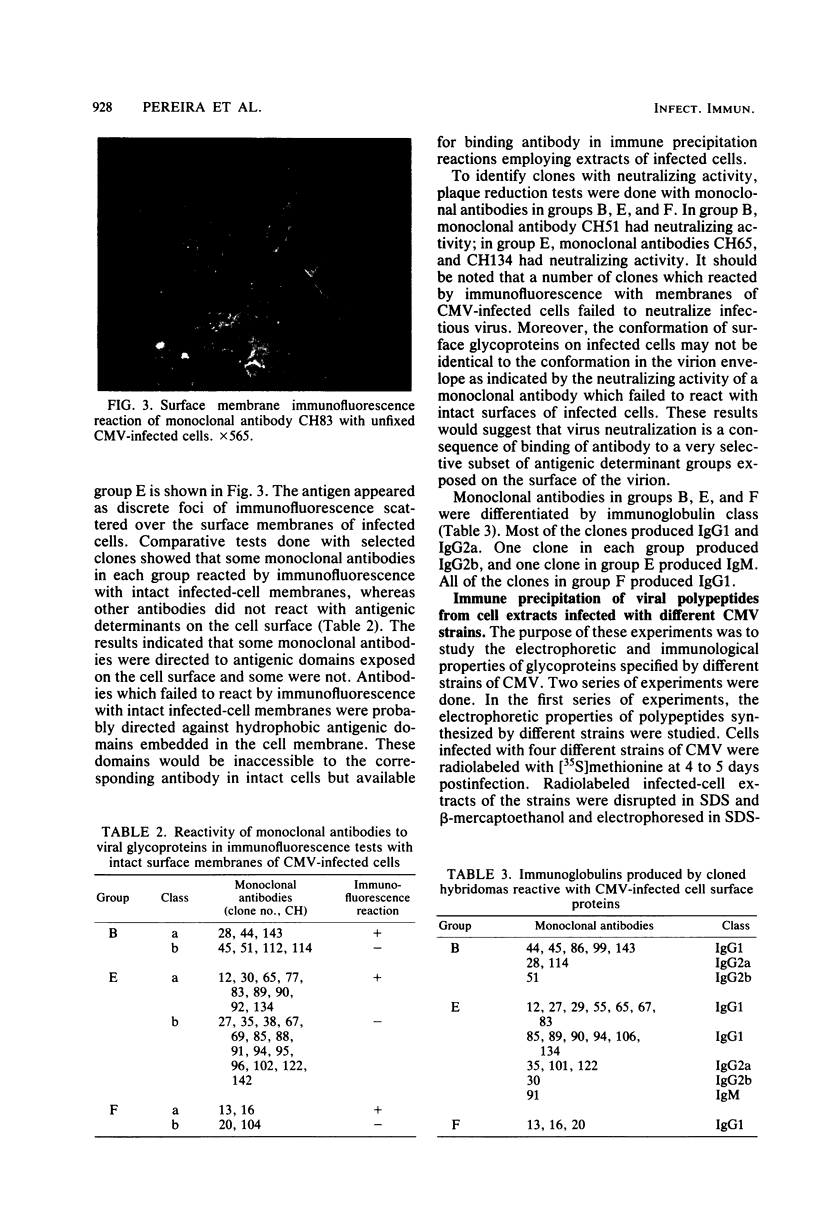
Seventy-seven clones of hybridomas selected for reactivity by immunofluorescence with human cytomegalovirus (CMV)-infected cells were produced by fusing mouse myeloma cells with the spleen cells of mice immunized with CMV strain AD169. The clones were classified into seven groups on the basis of the electrophoretic properties of the polypeptides immune precipitated from extracts of CMV-infected cells. Studies on the three groups of monoclonal antibodies directed against CMV surface membrane antigens showed the following. Clones in each group were differentiated by immunoglobulin subclass, neutralizing activity, and reactivity with the antigenic domains of proteins exposed on the surface membranes of intact CMV-infected cells. Monoclonal antibodies in each group precipitated one slowly migrating protein and multiple faster migrating forms which shared antigenic determinants. The first group of monoclonal antibodies precipitated four glycosylated polypeptides with apparent molecular weights of 130,000, 110,000, 100,000, and 60,000. Monoclonal antibody CH51 of this group neutralized infectious virus but failed to react with antigenic domains on the surfaces of infected cells. The second group of monoclonal antibodies precipitated four polypeptides with apparent molecular weights of approximately 66,000, 55,000, 50,000, and 46,000. Monoclonal antibodies CH65 and CH134 in this group had neutralizing activity and reacted with antigenic domains of proteins exposed on the surface of CMV-infected cells. The third group of monoclonal antibodies precipitated four polypeptides with apparent molecular weights of 49,000, 48,000, 34,000, and 25,000. Serological analysis of 15 naturally occurring CMV strains with a panel of monoclonal antibodies to surface membrane proteins showed that the antigenic determinants reactive with the antibodies tested were conserved in all of the strains. Monoclonal antibodies to surface membrane proteins on CMV-infected cells may prove to be valuable reagents for identification of virus isolates.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER P., MELNICK J. L., MAYOR H. D. A MORPHOLOGIC COMPARISON BETWEEN THE DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES OF HERPES ZOSTER AND HUMAN CYTOMEGALOVIRUS. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:11–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Harnish D., Killington R. A., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Monoclonal antibodies to two glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):438–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.438-446.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Long D., Pereira L., Hampar B., Zweig M., Cohen G. H. Effect of monoclonal antibodies on limited proteolysis of native glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.478-488.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Honess R. W., Heiner D. C., Heine J. W., Jr, Murnane J., Wallace R., Guze L. B. Cytomegalovirus proteins. I. Polypeptides of virions and dense bodies. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):243–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.243-254.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Antisera to human cytomegalovirus produced in hamsters: reactivity in radioimmunoassay and other antibody assay systems. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1184–1190. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1184-1190.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Structural and nonstructural proteins of strain Colburn cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):516–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., St Jeor S., Rapp F. Comparison of the polypeptides of several strains of human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):447–454. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Alford C. A., Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Pass R. F. Molecular epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infections in women and their infants. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 23;303(17):958–962. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010233031702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Huong S. M., Tegtmeier G. E., Alford C. Cytomegalovirus: genetic variation of viral genomes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:332–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Kilpatrick B. A., Huang Y. T., Pagano J. S. Detection of human cytomegalovirus and analysis of strain variation. Yale J Biol Med. 1976 Mar;49(1):29–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick B. A., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Analysis of cytomegalovirus genomes with restriction endonucleases Hin D III and EcoR-1. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):1095–1105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.1095-1105.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Sapienza V. J., Carp R. I., Moon H. M. Analysis of structural polypeptides of purified human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.604-611.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D. V., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D. Serological analysis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.363-367.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Norrild B., Roizman B. Differential immunologic reactivity and processing of glycoproteins gA and gB of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 made in Vero and HEp-2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Cremer N. Electrophoretic analysis of polypeptides immune precipitated from cytomegalovirus-infected cell extracts by human sera. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):933–942. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.933-942.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Type-common and type-specific monoclonal antibody to herpes simplex virus type 1. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):724–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.724-732.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., WATERMAN S., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. Cytopathogenic agent resembling human salivary gland virus recovered from tissue cultures of human adenoids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jun;92(2):418–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Abady I. The morphogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. Isolation and polypeptide characterization of cytomegalovirions and dense bodies. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):464–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira-Linhares M. I., Faucon-Biguet N., Chardonnet Y., Revillard J. P. Polypeptides and major antigens of four new isolates of cytomegalovirus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1981;169(3):197–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02123593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus: glycoproteins associated with virions and dense bodies. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):594–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.594-609.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Mocarski E. S., Thomsen D. R., Urbanowski M. L. Membrane glycoproteins and antigens induced by human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):119–129. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Sequence of protein synthesis in cells infected by human cytomegalovirus: early and late virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):686–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.686-701.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Synthesis of proteins and glycoproteins in cells infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):751–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.751-767.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waner J. L., Weller T. H. Analysis of antigenic diversity among human cytomegaloviruses by kinetic neutralization tests with high-titered rabbit antisera. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):151–157. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.151-157.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Rabin H., Hampar B. Shared antigenic determinants between two distinct classes of proteins in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):644–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.644-652.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]