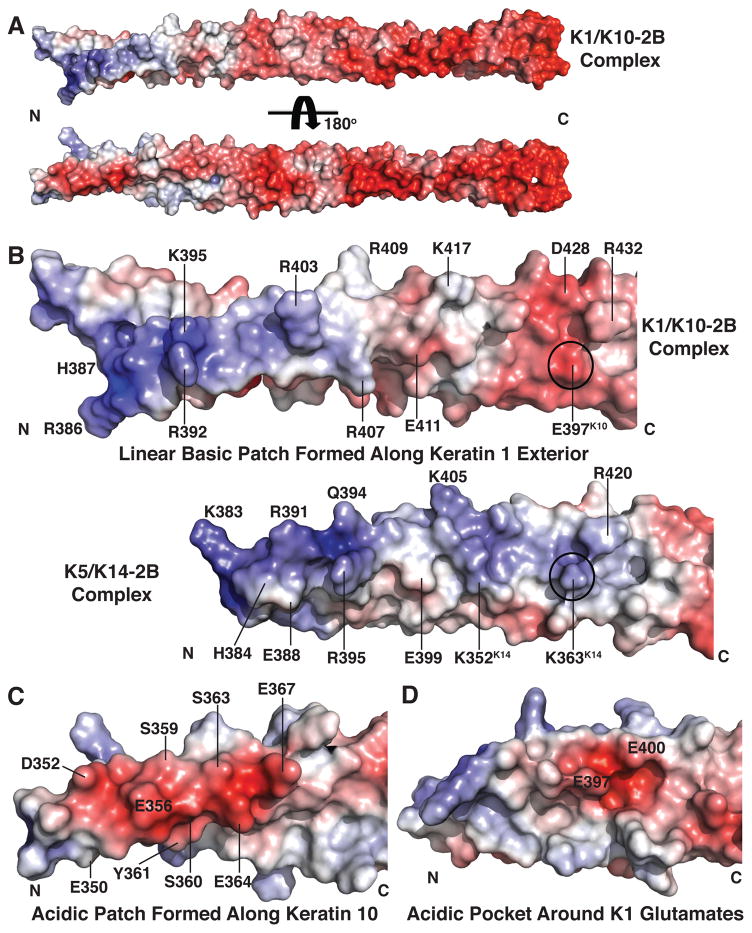
Fig. 2. Electrostatic surface properties of K1-K10-2B.
(a) K1-K10-2B heterodimer depicted in two orientations, related by 180°, demonstrating the 2B helix has polarization of charge: a mixed acidic and basic character at the N-terminus and predominantly acidic character at the C-terminus. (b) The N-terminal surface of K1-K10-2B is more acidic than the basal keratin complex K5-K14-2B because it contains a glutamate (Glu397K10) rather than lysine (Lys363K14) at homologous positions (circle). The K1-K10 and K5-K14 molecules are structurally aligned in the panel; there are 27 additional N-terminal residues observed in the K1-K10 structure. (c) Acidic patch formed along the N-terminal surface of K10-2B. (d) Acidic pocket formed between Glu397K1 and Glu400K1.