Table 2. Collective Variables (CVs) Biased in the RECT Simulations.
| simulation | residues with biases | CVs biased in each of the residuesa | additional biased CVsb | penaltyc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KF1 A | T11, T12, A13 | α, β, γ, ε, ζ, χ, pucker, base-coor. | ||
| 1KF1 B | T11, T12, A13 | α, β, γ, ε, ζ, χ, pucker, base-coor. | zg | |
| 1KF1 C | T11, T12, A13 | α, β, γ, ε, ζ, χ, pucker, base-coor. | dist G9(H22)-T11(O4) | |
| 1KF1 D | T11, T12, A13 | α, β, γ, ε, ζ, χ, pucker, base-coor. | dist G9(H22)-T11(O4) | zg |
| 2GKU A | T6, T7, A8 | α, β, γ, ε, ζ, χ, pucker, base-coor. | ||
| 2MBJ A | T13, T14, A15 | α, β, γ, ε, ζ, χ, pucker, base-coor. | ||
| 2MBJ B | T13, T14, A15 | α, β, γ, ε, ζ, χ, pucker, base-coor. | dist. G11-T14 |
α, β, γ, ε,
ζ, and χ = dihedral angles; pucker = x-axis component of pucker; “base-coor.’’ = nucleobase
coordination number i.e. number of nucleobases in proximity of the
corresponding nucleobase (each nucleobase is approximated by its center
of mass), computed using 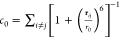 , where r0 =
4Å.
, where r0 =
4Å.
dist = distance; measured either between selected atoms (in parentheses) or nucleobases’ centers of mass.
zg = flat-well potential function applied on ζ(G10) and γ(T11) (Figures S2 and S3).
