Figure 5.
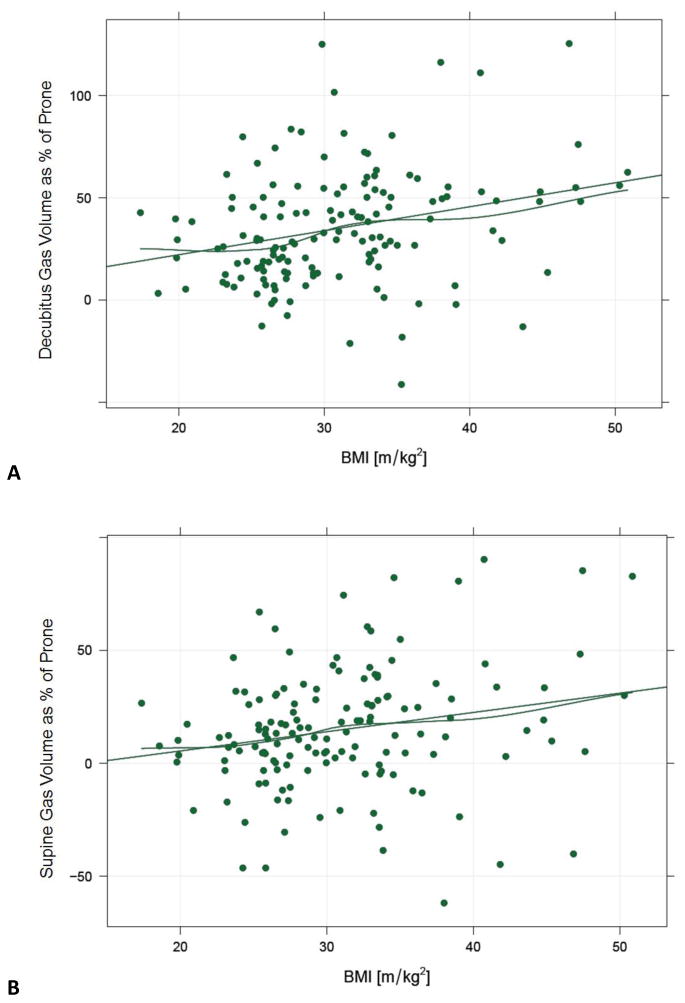
Correlation between colonic distention by position and patient BMI.
Graphs depicting decubitus (A) and supine (B) gas volume as a percentage difference compared with the prone volume, plotted against BMI. Values above zero indicate a higher volume than the prone scan. As BMI increases, the degree of improvement in decubitus and supine distention increases further. Correlations are 0.280 (p<0.001) and 0.213 (p<0.001), respectively. The straight lines represent the least squares fit and the wavy lines apply a local smoother. In general, the percentage increase in distention is greater in the decubitus position at all BMI values.
