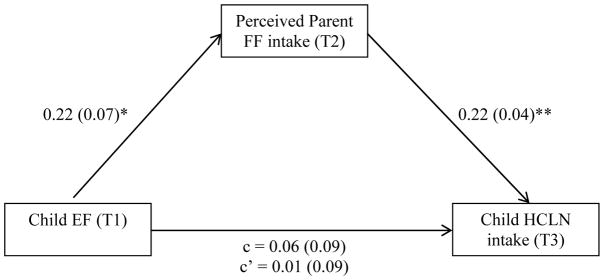
Figure 1. Longitudinal Direct and Indirect Effects of Child EF on Perceived Parent Fast Food Intake and HCLN intake.
Indirect effect = 0.05, SE = 0.02, 95% CI = (0.02/0.10)
R2 = 0.23; F(7, 840) = 36.23, p < 0.001
N = 848
* p < 0.01
** p < 0.001
Note: Covariates include child gender (male = 1, female = 0, B = 0.01, SE = 0.06, p = 0.90), Hispanic ethnicity (B = 0.06, SE = 0.07, p = 0.34), free/reduced lunch status (B = 0.33, SE = 0.07, p < 0.001), program group (B = 0.15, SE = 0.06 p < 0.05) and baseline child HCLN intake (B = 0.35, SE = 0.03, p < 0.001); unstandardized parameter estimates are reported with standard errors in parentheses; higher EF scores indicate more EF difficulties.