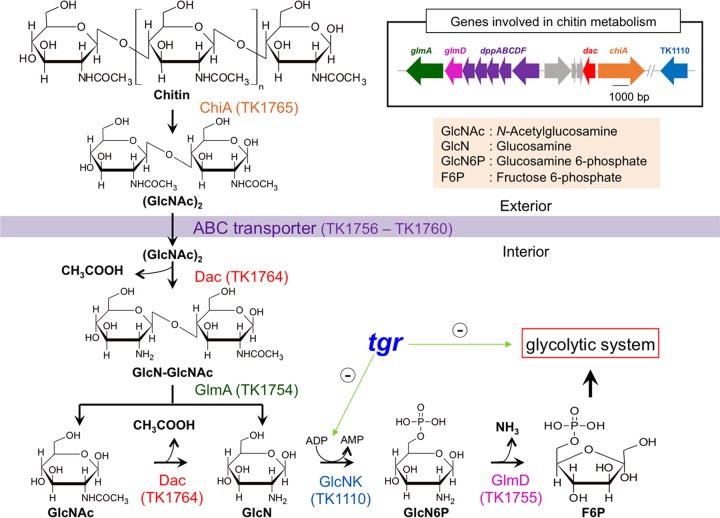
FIG 1.
Chitin metabolic pathway of T. kodakarensis. Chitin is converted into N-,N′-diacetylchitobiose, (GlcNAc)2, by extracellular chitinase (ChiA) encoded by the TK1765 gene. An ABC transporter (DppABCDF) encoded by the genes at locus TK1756 to TK1760 may allow (GlcNAc)2 to enter into the cell, where deacetylation of the nonreducing end occurs by diacetylchitobiose deacetylase (Dac) encoded by the TK1764 gene. Exo-β-d-glucosaminidase (GlmA) encoded by the TK1754 gene hydrolyzes the product (GlcN-GlcNAc) to glucosamine (GlcN) and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). Dac further converts GlcNAc to GlcN with release of one more acetate. In T. kodakarensis, there is no homolog for GlcN kinase (GlcNK) that produces glucosamine 6-phosphate (GlcN6P), but this reaction is thought to be performed by an ADP-dependent glucokinase encoded by the TK1110 gene. GlcN6P is further deaminated, leaving ammonium, by GlcN6P deaminase (GlmD) encoded by the TK1755 gene. The fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) formed in this reaction further enters into the glycolytic pathway. Tgr is a transcriptional repressor for glycolytic genes including TK1110 (green arrows with minus signs represent effects of Tgr on transcriptional repressions of glycolytic genes).