Figure 1.
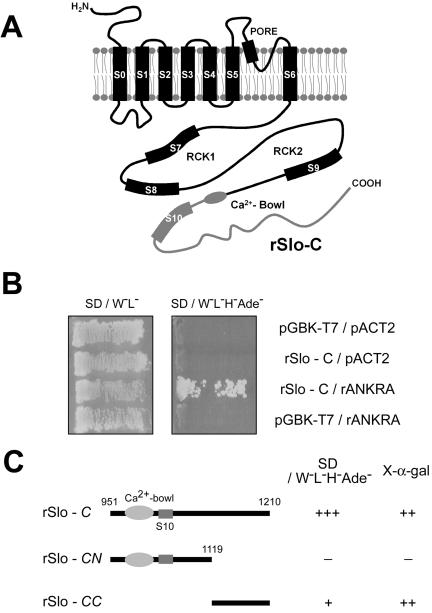
Carboxy terminus of rSlo recruits an Ankyrin-repeat family A protein, rANKRA, in yeast two-hybrid screening. (A) Putative membrane topology of rSlo (α-subunit of large conductance Ca2+-activated potassium channel) protein. Cloned rSlo channel (AF135265) has seven membrane-spanning segments, including voltage-sensing S4, two regulating the conductance of K+ (RCK) domains, and “Calcium-Bowl” (a negatively charged region to be implicated in calcium binding). One-third of cytosolic C terminus (rSlo-C, amino acids 951-1210, gray line) including Calcium-Bowl was used to screen rat brain library (MATCHMAKER cDNA library; BD Biosciences). (B) Yeast, AH109 was transformed simultaneously with the two indicated plasmids, and cotransformants were selected on SD media lacking tryptophan and leucine. The interaction was monitored by histidine and adenine prototrophy. Yeasts only cotransformed with rSlo-C and rANKRA could survive on the SD/W-L-H-Ade- plate. (C) Using rSlo-C, -CN, and -CC domains as baits, region involved in recruiting rANKRA was investigated in yeast. Yeast cells harboring rSlo-C and rSlo-CC in bait vector were survived on selection media SD/W-L-H-Ade- containing X-α-gal (marked as +) and showed blue color with rANKRA in prey vector. Calcium-Bowl and S10 segment are indicated in molecular cartoon.