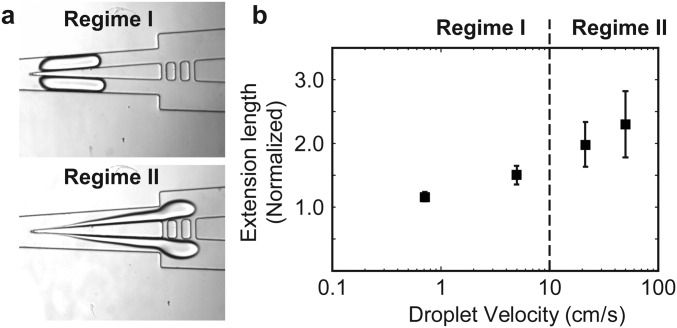
Fig. S3.
Effect of flow rate on a shear-thinning viscoelastic droplet. The drop consisted of methylcellulose solution (2% wt/vol), and the continuous phase consisted of HFE-7500 containing EA surfactant (2% wt/wt). The infinite rate viscosity of the drop solution was measured as described in SI Materials and Methods to be 900 cP. (A) Snapshots of the drop in regime I and II. The definition of the two regimes was the same as that in the text for a cell. (B) Extension length of the drop as a function of the velocity of the drop. We note that similar transition in droplet shape occurred with increasing flow rate in a Newtonian droplet consisting of water or a glycerol solution (20% wt/wt), except that in regime II the rear end of the drop often broke into smaller drops instead of forming a long thread hanging at the knife.