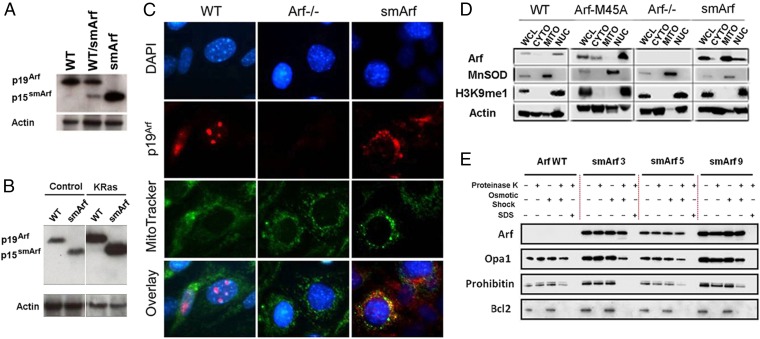
Fig. 1.
p15smArf localizes within the mitochondria of primary MEFs. (A) p15smArf is not normally detected by immunoblotting in wild-type MEFs because of its rapid turnover, but it accumulates when translation is efficiently initiated at M45. (B) Infection of MEFs with a retroviral vector encoding a KRas (G12V) oncoprotein induces the Arf promoter to yield increased levels of Arf proteins; even under this condition, p15smArf is only barely detected in WT Arf+/+ cells. The four lanes illustrated were cropped, two by two, from a single immunoblot developed after a single exposure. Actin was used as a protein loading control. (C) For immunofluorescence, cells were treated with membrane-permeable MitoTracker (green) (Invitrogen), fixed, stained with 5C3-1 monoclonal antibody to p19Arf followed by goat anti-rat Ig (red), and counterstained with DAPI (blue) to visualize nuclei. p19Arf expressed in WT cells localizes to nucleoli, whereas p15smArf colocalizes with Mitotracker (green) in mitochondria. (D) Subcellular fractionation confirms mitochondrial (MITO) enrichment of p15smArf together with superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), whereas p19Arf colocalizes in the nuclear (NUC) fraction with H3K9me1-marked histones. Fractionation experiments were performed with three independently derived MEF clones of each indicated genotype; representative data are illustrated. Fractionated organelles from whole cell lysates (WCL) were denatured in loading buffer, and equal amounts of protein loaded in each lane were separated on SDS/PAGE gels and immunoblotted (43). Antibodies to MnSOD (BD Biosciences), histone H3K9me1 (Invitrogen), and actin (Millipore) were used to chart enrichment of organelles in different fractions. Signals for p19Arf and p15smArf, simply indicated at the left as Arf, were aligned for convenient illustration despite their different electrophoretic mobilities on denaturing gels. (E) p15smArf localizes within the mitochondrial matrix. Purified mitochondria (42) were treated as described (23) with proteinase K to remove exposed proteins. Osmotic shock disrupted the OMM, and SDS solubilized the OMM and IMM to release matrix components. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting by using submitochondrial markers including BCL2 (OMM), Opa1 (IMM and intramembrane space), and Prohibitin (inner matrix). Three primary MEF strains designated −3, −5, and −9 expressing smArf were analyzed in parallel on a single gel together WT Arf+/+ cells.