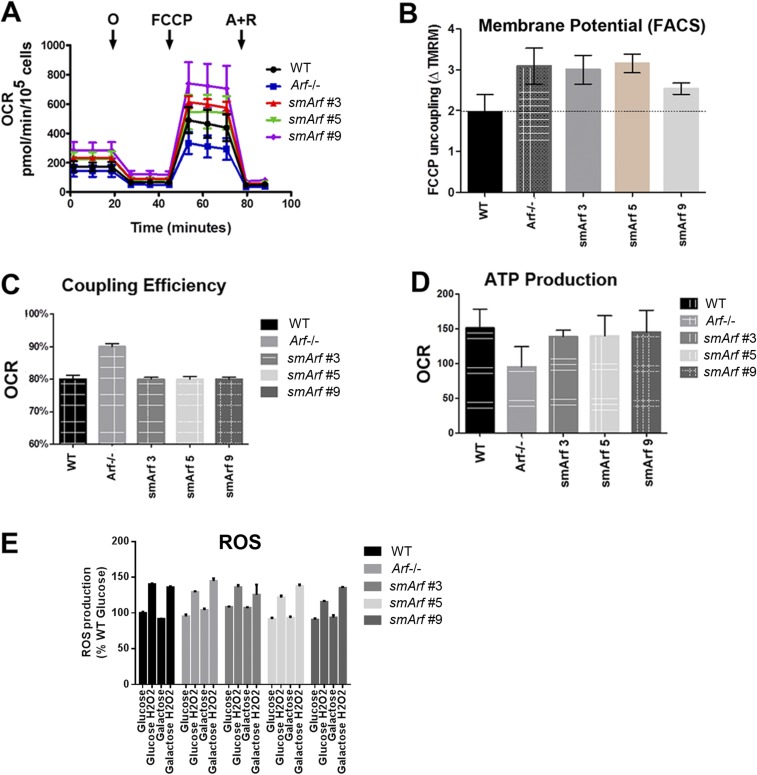
Fig. S1.
Mitochondrial function in MEFs of various Arf genotypes. (A) Measurements of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) were made with a Seahorse Xfe24 Bioanalyzer (Agilent) as per manufacturer’s instructions. Oligomycin (O) was used to poison complex V of the electron transfer chain (ETC); FCCP (carbonyl cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-hydrazone), a protonophore added to collapse the inner membrane gradient, was used to allow the ETC to function at its maximal rate; and antimycin A plus rotenone (A+R) were added to shut down ETC function to reveal residual nonmitochondrial respiration. ATP-linked respiration is calculated by subtracting the oligomycin rate from baseline cellular OCR, whereas proton leak respiration is calculated by subtracting nonmitochondrial respiration from the oligomycin rate. Mitochondrial reserve capacity is calculated by subtracting basal respiration from maximal respiratory capacity. These studies indicated that Arf inactivation decreased overall oxygen consumption, whereas three independently derived smArf MEF strains exhibited slightly higher average oxygen consumption than WT cells, rescuing the deficiencies in ATP production and maximal respiratory capacity of Arf-null MEFs. (B) When MEFs were stained with 2.5 µM tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester (TMRM, detected by FACS at 574 nm) and normalized to TMRM-stained cells treated with FCCP, Arf-deficient and smArf cells displayed subtly increased mitochondrial membrane potential compared with the WT strain, differing from the decreased membrane potential reported for cells acutely transfected with smArf cDNA (14). (C) Seahorse analysis of Arf-null MEFs revealed an increased coupling efficiency compared with smArf and WT strains. The coupling efficiency is defined as the proportion of the oxygen consumed to drive ATP synthesis compared with that driving proton leak respiration and is calculated as the fraction of basal mitochondrial OCR used for ATP synthesis (ATP-linked OCR/basal OCR). (D) WT and smArf MEFs were indistinguishable with regard to ATP-related oxygen consumption. Taken together, smArf MEFs manifest similar respiratory capacity to WT MEFs. (E) WT, Arf-null, and smArf MEFs plated in 96-well dishes were treated with either glucose- or galactose-containing medium for 4 h. ROS was induced with 1 mM H2O2 and measured by using ROS red stain solution (Abcam) on a Beckman Coulter microplate reader. Upon oxidation, the staining solution emits fluorescence at Ex/Em 520/605 nm. Results were normalized to WT ROS levels in glucose. No significant differences were detected between genotypes.