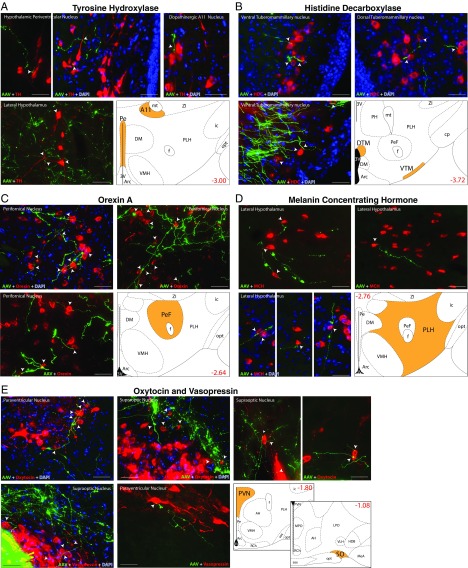
Fig. 3.
Retinal innervation of hypothalamic neurons containing the neurotransmitters dopamine and histamine and the neuropeptides orexin, MCH, oxytocin, and vasopressin. (A) Immunopositive TH neurons (red) in close apposition to retinal axons and varicosities (green). (B) Immunopositive histaminergic neurons in close apposition to retinal axons and varicosities. (C) Immunopositive orexinergic neurons in close apposition to retinal axons and varicosities. (D) Immunopositive MCH neurons in close apposition to retinal axons and varicosities. (E) Immunopositive oxytocinergic and vasopressinergic neurons in close apposition to retinal axons and varicosities. Reconstructions in lower right panels show locations of neurons in the different hypothalamic areas and nuclei. Numbers in red indicate distance from bregma. Arrowheads point to close appositions. (Scale bars: 50 μm.) Arc, arcuate nucleus; cp, cerebral peduncle; DM, dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus; DTM, dorsal tuberomammillary nucleus; f, fornix; HDB, horizontal limb of the diagonal band; ic, internal capsule; LPO, lateral preoptic area; MeA, medial amygdaloid nucleus; MPO, medial preoptic nucleus; mt, mammillothalamic tract; opt, optic tract; Pe, periventricular nucleus; PH, posterior hypothalamic nucleus; PLH, peduncular part of the LH; RCh, retrochiasmatic area; SO, supraoptic nucleus; sox, supraoptic decussation; VLH, ventrolateral hypothalamic nucleus; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; VTM, ventral tuberomammillary nucleus; ZI, zona incerta; 3V, third ventricle. Other abbreviations are defined in Fig. 2.