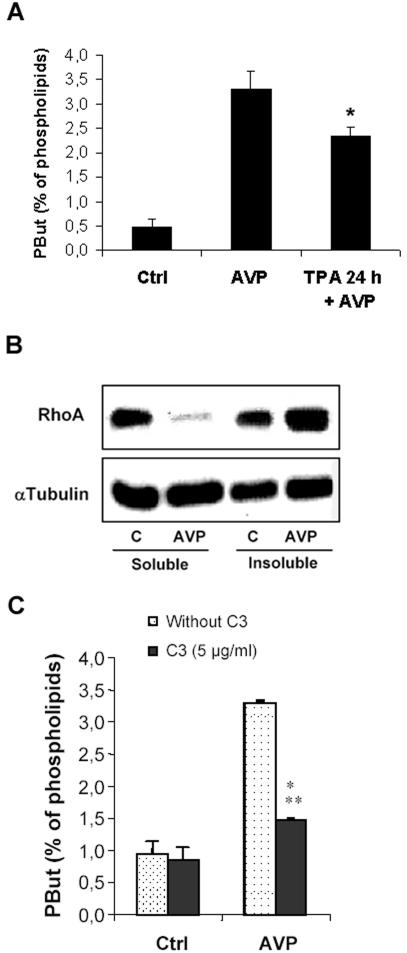
Figure 1.
AVP activates PLD in L6 cells mainly through Rho pathway. (A) PLD activity in L6 cells, as evaluated by phosphatidylbutanol formation in intact cells. The cells were labeled with [3H]palmitate, treated or not (control) for 30 min with 10-7 M AVP, in the presence of 1% butanol, before lipid extraction and analysis. When required, the cells were pretreated by 10-7 M TPA for 24 h. *, different from treatment by AVP alone, p < 0.05 (n = 3). (B) Immunoblotting of RhoA protein in soluble versus insoluble cell fractions. The cells were treated or not (control) by 10-7 M AVP for 1 min before harvesting, homogenizing, and fractionating the extracts by ultracentrifugation. Equal amounts of proteins from each fraction (30 μg) were deposited on SDS gels. The blots were probed with a RhoA-specific antibody, stripped, and reprobed with a tubulin-specific antibody to assess equal loadings. (C) Effect of C3 exoenzyme on AVP-induced PLD stimulation. The cells were scraped off and treated or not in suspension by C3 exoenzyme. After plating, they were challenged or not (control) with 10-7 M AVP and PLD activity was assayed. ***, different from C3-untreated cells, p < 0.0001, n = 3.