Figure 2. No major role of the P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors in ATP-induced increase in the [Ca2+]i in Huh-7 cells.
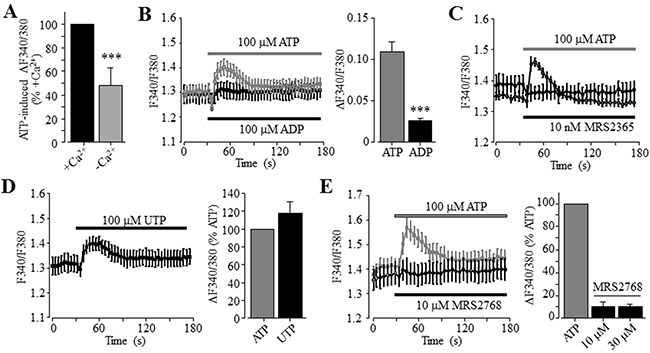
(A) Summary of 100 μM ATP-induced peak increase in the [Ca2+]i in the extracellular Ca2+-containing and Ca2+-free solutions, expressed as % of that induced by ATP in the extracellular Ca2+-containing solution, from three independent experiments. (B) Left, representative recordings of Ca2+ responses induced by 100 μM ATP (grey) and ADP (black) in the extracellular Ca2+-containing solutions, with six wells of cells for each case. Right, summary of the peak increase in the [Ca2+]i.***, p < 0.001 (A and B). (C) Representative recordings of Ca2+ responses induced by 100 μM ATP (grey) and 10 μM MRS2365 (black) in the extracellular Ca2+-containing solution, from six wells of cells for each concentration. (D) Left, representative recordings of Ca2+ responses induced by 100 μM UTP in the extracellular Ca2+-containing solution with six wells of cells for each case. Right, summary of UTP-induced peak increase in the [Ca2+]i, expressed as % of that induced by 100 μM ATP, from three independent experiments. (E) Left, representative recordings of the Ca2+ responses induced by 10 μM MRS2768 (black) and 100 μM ATP (grey) in the extracellular Ca2+-containing solution with six wells of cells for each case. Right, summary of MRS2768-induced peak increase in the [Ca2+]i, expressed as % of that induced by 100 μM ATP, from three independent experiments.
