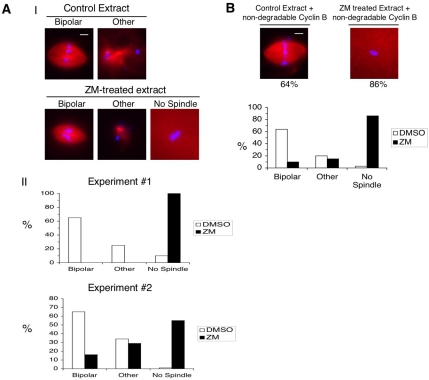
Figure 5.
ZM reduces spindle assembly in extracts driven into M phase by CSF extract or nondegradable cyclin B protein. (A) Extracts were prepared from metaphase II-arrested eggs (CSF extract) and supplemented with rhodamine-labeled tubulin and sperm nuclei (500/μl). Extracts were driven into interphase by the addition of calcium chloride. Sixty minutes after calcium addition, DMSO (control) or ZM was added. Twenty minutes later, control and ZM-treated extracts were driven into M phase by the addition of CSF extract containing either DMSO or ZM, respectively. Samples were fixed at 80 min after M phase initiation and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. The number of bipolar-type spindles (Bipolar), spindles that were not obviously bipolar (Other), or nuclei that lacked detectable microtubule staining (No Spindle) were determined. The images in panel I represent the different categories that were quantified in panel II. The inhibitory effect of ZM on spindle assembly varied between experiments. The quantification of spindle structures from two independent experiments is shown in panel II. More than 100 structures were counted for each experiment. Bar, 15 μm. (B) CSF egg extract was treated as in A except that nondegradable cyclin B protein was added to drive the extract into mitosis instead of CSF extract. Spindle structures were counted as in A. Bar, 15 μm. More than 100 structures were counted in this experiment. The graph showing the percentage of spindle structures observed in DMSO- and ZM-treated extracts is a representative of three independent experiments.